중심단어
Lymphangiogram, Lymphatic leakage
임상소견
음경의 악성흑색종으로 음경절제술을 받고 우측 심부 서혜부 임파선절제술을 시행 받았음. 시술 후 3주 후에 우측 서혜부 임파선절제술 받은 부위에 생긴 lymphocele 절제술을 받았으나 그 이후 하루에 거즈 7 팩 정도 교체가 필요할 정도로 절제술 부위에 lymphatic leakage가 생김
진단명
Lymphatic leakage after lymph node dissection at the right inguinal area
영상소견
전산화 단층촬영에서 우측 서혜부에 lymphocele이 있으며 (Fig. 1A) 이에 대한 수술적 절제술에도 불구하고 계속적인 lymphatic leakage가 있었다.
시술방법 및 재료
Pedal lymphangiogram을 시행하기 위해 시술하고자 하는 발의 첫 번째부터 세 번째 발가락 사이 공간을 리도카인으로 국소 마취한 후 10mL의 indigo carmine (Korea United Pharm. INC, Seoul, Korea)을 같은 부위에 피하조직에 주사하였다. 20–30분 후에 발 등에서 염색된 lymphatics 중 first metatarsal bone base에서 가장 두드러진 lymphatic vessel을 박리하고자 하였다. Transverse incision 후에 주위 조직을 박리하고 염색된 lymphatic vessel을 박리하여 30-G LG needle (Cook Inc, Bloomington, IN, USA)을 써서 cannulation하였다. Needle과 lymphatic vessel을 3–0 silk thread로 묶었다. 그 후 7mL의 lipiodol을 총 20분에 걸쳐서 서서히 주입하였다.
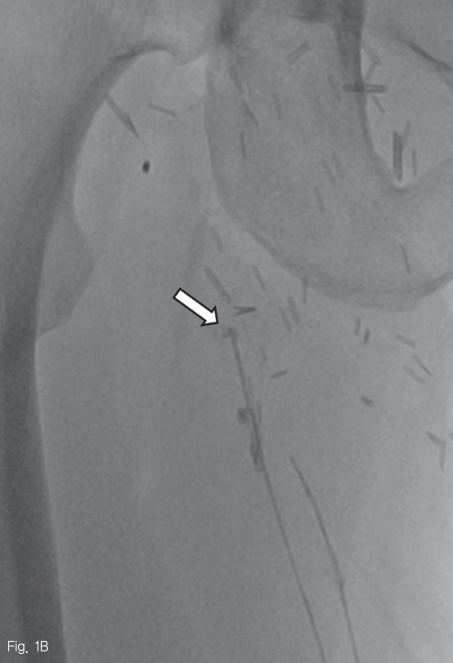
Pedal lymphangiogram 시행, 약 30분 후에 얻은 영상에서 우측 서혜부의 개방성 창상 부위 입구에서 lymphatics가 끊어져 있고 lipiodol 누출이 보였다 (Fig. 1B). Lipiodol 주입 14 시간 후에도 lipiodol 누출이 여전히 보였고 (Fig. 1C), 20시간 후 얻은 CT 영상에서도 lymphatic이 끊어진 양상이 보였다 (Fig. 1D).
Fig 1A
45-year-old man with right inguinal area swelling after deep inguinal lymph node dissection.
A. An axial CT scan shows a lymphocele (asterisk), which was subsequently dissected, in the right inguinal area. Note the minimal fluid collection at the left superficial inguinal lymph node dissection site.
B. A radiographic image obtained 30 minutes following lipiodol injected into the lym phatics of the dorsum of the foot, shows disruption of the lymphatic with lipiodol leakage (arrow) at the entrance of the open wound in the right inguinal area.
C. A radiographic image obtained 14 hours following lipiodol injection, still shows a leakage point (arrow).
D. A CT scan obtained 20 hours following lipiodol injection, shows the disrupted lymphatic (arrow). The leakage was eliminated five days following lymphangiography.
Fig 1B
45-year-old man with right inguinal area swelling after deep inguinal lymph node dissection.
A. An axial CT scan shows a lymphocele (asterisk), which was subsequently dissected, in the right inguinal area. Note the minimal fluid collection at the left superficial inguinal lymph node dissection site.
B. A radiographic image obtained 30 minutes following lipiodol injected into the lym phatics of the dorsum of the foot, shows disruption of the lymphatic with lipiodol leakage (arrow) at the entrance of the open wound in the right inguinal area.
C. A radiographic image obtained 14 hours following lipiodol injection, still shows a leakage point (arrow).
D. A CT scan obtained 20 hours following lipiodol injection, shows the disrupted lymphatic (arrow). The leakage was eliminated five days following lymphangiography.
Fig 1C
45-year-old man with right inguinal area swelling after deep inguinal lymph node dissection.
A. An axial CT scan shows a lymphocele (asterisk), which was subsequently dissected, in the right inguinal area. Note the minimal fluid collection at the left superficial inguinal lymph node dissection site.
B. A radiographic image obtained 30 minutes following lipiodol injected into the lym phatics of the dorsum of the foot, shows disruption of the lymphatic with lipiodol leakage (arrow) at the entrance of the open wound in the right inguinal area.
C. A radiographic image obtained 14 hours following lipiodol injection, still shows a leakage point (arrow).
D. A CT scan obtained 20 hours following lipiodol injection, shows the disrupted lymphatic (arrow). The leakage was eliminated five days following lymphangiography.
Fig 1D
45-year-old man with right inguinal area swelling after deep inguinal lymph node dissection.
A. An axial CT scan shows a lymphocele (asterisk), which was subsequently dissected, in the right inguinal area. Note the minimal fluid collection at the left superficial inguinal lymph node dissection site.
B. A radiographic image obtained 30 minutes following lipiodol injected into the lym phatics of the dorsum of the foot, shows disruption of the lymphatic with lipiodol leakage (arrow) at the entrance of the open wound in the right inguinal area.
C. A radiographic image obtained 14 hours following lipiodol injection, still shows a leakage point (arrow).
D. A CT scan obtained 20 hours following lipiodol injection, shows the disrupted lymphatic (arrow). The leakage was eliminated five days following lymphangiography.
추적관찰
시술 후 개방성 창상 부위에서 배액되는 양이 많이 감소하였으며 5일 후에는 멈추었다.
고찰
Lipiodol을 이용한 lymphangiogram이 lymphatic leakage를 감소시킬 수 있음은 잘 알려져 있으며 그 기전을 명확히 밝히기는 어려우나 유출된 lipiodol이 inflammatory and granulomatous reaction과 lymphatic vessel 내부와 바깥으로 유출된 lipiodol의 색전 효과로 설명된다.
Lymphangiogram은 발등의 lymphatic vessel을 박리하여 lipiodol을 주입하는 pedal lymphangiogram이 있고, 서혜부위의 lymph node를 직접 천자하여 lipiodol을 주입하는 intranodal lymphangiogram이 있다. Pedal lymphangiogram은 보다 침습적이고 시간도 오래 걸리는 단점이 있으나 두 lymphangiogram 간의 효과에 대해서는 우월을 가리기 어렵다. 본 증례의 경우에는 서혜부에서의 lymphatic leakage가 문제여서 intranodal lymphangiogram은 불가능하며 pedal lymphangiogram으로만 해결될 수 있었던 경우였고 5일 후에 배액이 멈추어서 좋은 효과를 보였던 경우이다.
본 증례와 같은 free lymphatic leakage 외에도 chylothorax, chylous ascites 등에도 효과가 좋은 것으로 되어 75–78%의 leakage site를 발견하는 것으로 보고되었다.
Pedal lymphangiogram은 발등에 수술적 절제가 필요하여 감염과 통증의 위험이 있다. 심각한 합병증으로는 intra-alveolar hemorrhage, lipiodol emboli in the pulmonary vasculature, allergic reactions to lipiodol, and extravasation of lipiodol into the soft tissue 등이 생길 수 있다.
참고문헌
1. Guermazi A, Brice P, Hennequin C, Sarfati E. Lymphography: an old technique retains its usefulness. Radiographics 2003;23:1541-1558; discussion 1559-1560
2. Matsumoto T, Yamagami T, Kato T, et al. The effectiveness of lymphangiography as a treatment method for various chyle leakages. Br J Radiol 2009;82:286-290
3. Kos S, Haueisen H, Lachmund U, Roeren T. Lymphangiography: forgotten tool or rising star in the diagnosis and therapy of postoperative lymphatic vessel leakage. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2007;30:968-973
4. Deso S, Ludwig B, Kabutey NK, Kim D, Guermazi A. Lymphangiography in the diagnosis and localization of various chyle leaks. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2012;35:117-126
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by