중심단어
Iatrogenic arterial injury, pseudoaneurysm, central venous catheterization
임상소견
5년 전 hypothyroidism 진단받고 치료 중 medication을 자의로 중단한 환자로, acute hepatitis로 입원 치료 중 azotemia가 점차 진행되어 permanent catheter를 insertion함. 시술 이후 permanent catheter insertion site 부위로 oozing이 발생하였고, oozing site를 지속적으로 compression함에도 불구하고 oozing이 aggravation되었음.
진단명
Iatrogenic pseudoaneurysm after central venous catheterization
영상소견
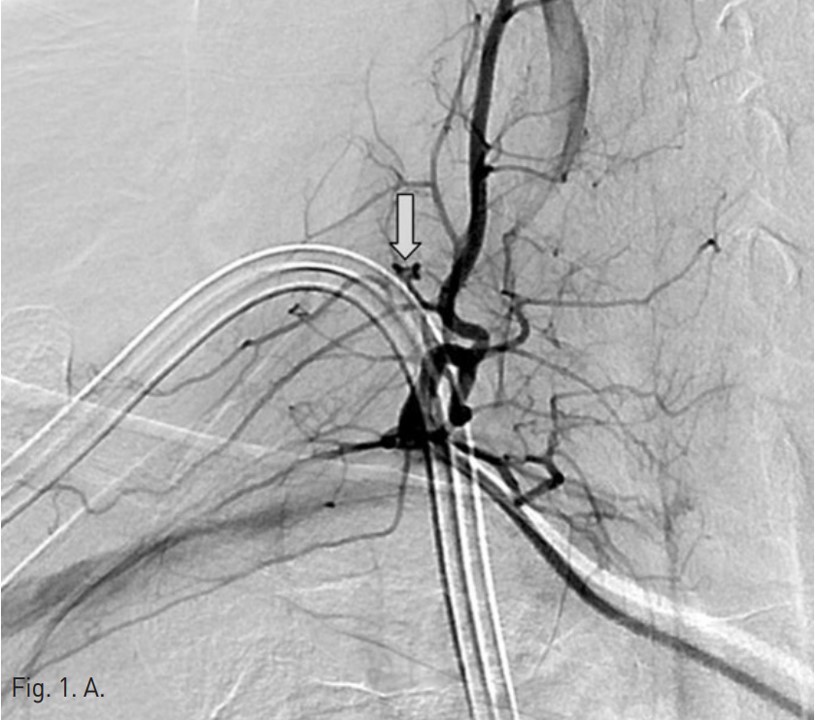
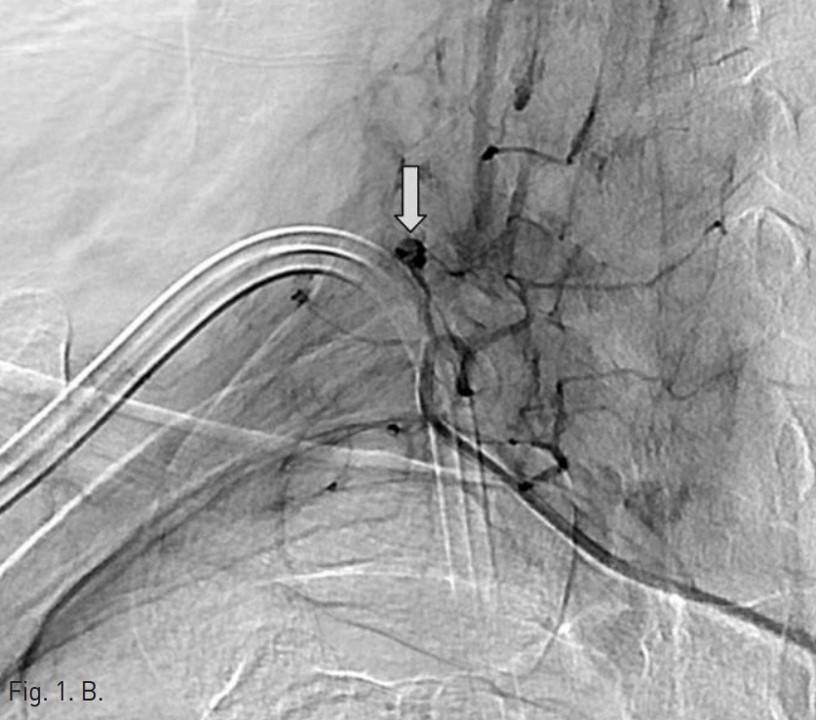
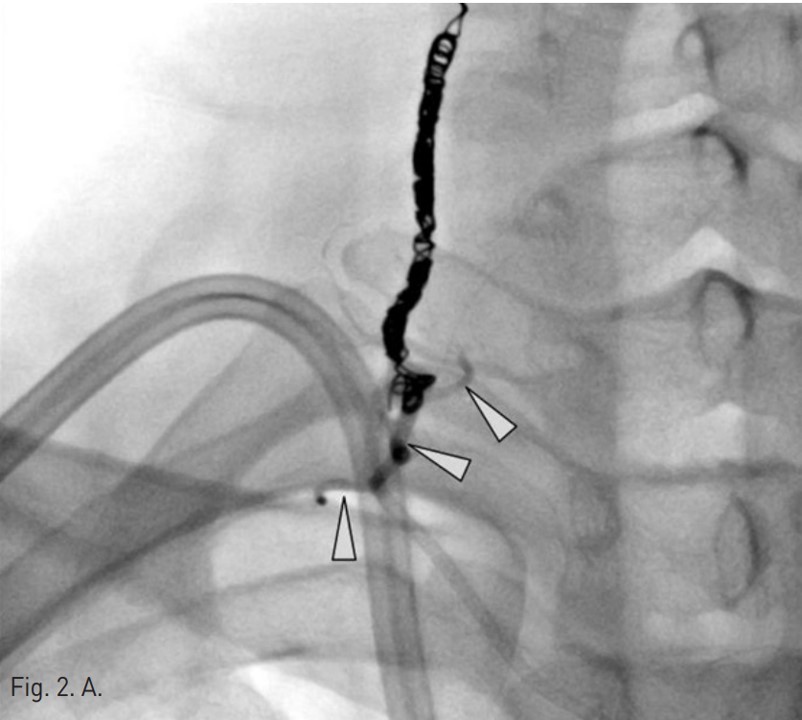
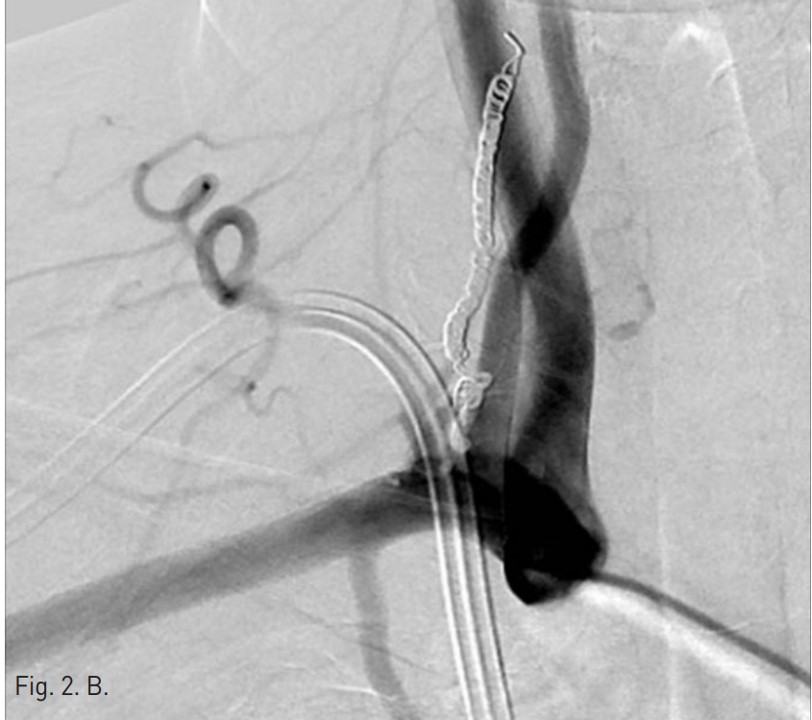
Permanent catheter insertion 이후 일주일 뒤 시행한 혈관조영술에서 갑상목동맥(right thyrocervical trunk)의 branch에 작은 거짓동맥류(small pseudoaneurysm)가 있고 permanent catheter를 insertion하는 과정에서 비롯된 합병증으로 판단되었음(Fig. 1A,B). 따라서 갑상목동맥의 기시부에서부터 아래 갑상동맥(inferior thyroidal artery)의 기시부까지 색전술을 시행하기로 함. Microcoil 및 glue를 사용하여 embolization 시행 후 조영제 검사에서 거짓동맥류는 보이지 않고(Fig. 2A,B) 임상 소견도 모두 호전되었음.
시술방법 및 재료
오른쪽 서혜부를 국소 마취 후 오른쪽 대퇴동맥을 천자하여 대동맥으로 카테터삽입술을 시행함. 그 후 guidewire를 통해 오른쪽 쇄골하 동맥 (right subclavian artery) 으로 진입하였고 조영술을 시행하여 갑상목동맥의 한 분지에 작은 거짓동맥류가 있는 것을 확인하였음(Fig. 1A,B). 이어서 2.2-F microcatheter with microwire(Progreat catheter, 150cm and Gold tip wire, Terumo)를 이용하여 거짓동맥류가 있는 분지로 진입하려 하였으나 혈관의 tortuosity가 심하여 시행하지 못함. 그래서 아래 갑상동맥의 기시부에서부터 갑상목동맥의 기시부까지 색전술을 시행하기로 하였고, microwire(Fathom, 0.016 inch, 160 cm, Cook)를 이용하여 아래갑상동맥으로 진입함.
아래갑상동맥의 원위부의 색전을 방지하기 위해서 한 개의 coil(F-IDC 2D 3x6cm, Boston scientific)이 사용되었고 아래갑상동맥의 기시부에 색전술을 시행하였음. 그 후에 아홉 개의 microcoil(Tornado microcoil, Cook)과 one vial의 glue(Histoacryl 0.5cc)를 이용하여 아래갑상동맥과 갑상목동맥에 색전술을 시행함.
색전술 후 혈관조영에서 오른쪽 갑상목동맥은 성공적으로 색전이 되었고 더 이상 거짓동맥류는 보이지 않았음(Fig. 2A,B).
고찰
Central line insertion과 같은 침습적 procedure의 증례가 많아짐에 따라 이에 따른 합병증도 함께 증가하고 있다. 이러한 합병증의 비율은 0.4 % 에서부터 9.9 %까지 다양하게 보고된 바 있으며, 그 예로서 hematoma formation, arterial dissection, thrombosis, respiratory compromise, nerve injury, arteriovenous fistula 그리고 pseudoaneurysm 등이 있을 수 있다. 그러나 본 증례와 같은 inadvertent arterial puncture의 경우는 흔하지 않은 것으로 되어 있다 (0.1-0.4%). 이러한 complication의 risk factor로는 obesity, short neck 그리고 emergency procedure 등이 보고되었다.
Arterial pseudoaneurysm은 전형적으로 시술 후 수일 내에 pulsatile mass가 발생하며, duplex ultrasonography가 pseudoaneurysm의 size와 origin을 파악하는 데 도움이 될 수 있다. 또한 혈관조영술도 종종 injury site를 명확하게 파악하기 위해 시행된다.
치료로는 stent-graft placement, percutaneous suture device, external compression after angiography, balloon occlusion 등의 technique이 있을 수 있고 severe한 경우 open repair도 고려해 볼 수 있다.
본 증례는 permanent catheter insertion 과정 중에 발생한 arterial injury로서, pseudoaneurysm을 coil 및 glue를 이용하여 성공적으로 embolization하였고 시술 후 부작용은 없었다.
참고문헌
1. Pikwer A, Acosta S, Kolbel T, Malina M, Sonesson B, Akeson J. Management of inadvertent arterial catheterization associated with central venous access procedures. Eur J Vasc Endovasc Surg 2009; 38:707-714
2. Cayne NS, Berland TL, Rockman CB, et al. Experience and technique for the endovascular management of iatrogenic subclavian artery injury. Ann Vasc Surg 2010; 24:44-47
3. Luckraz H. Venous pseudo-aneurysm as a late complication of short-term centraI venous catheterization. Cardiovascular Ultrasound 2003; 1:6
4. Bernik TR, Freidman SG, Scher LA, Safa T. Pseudoaneurysm of the subclavian-vertebral artery junction. Case report and review of the literature. Vas and endovas Sur 2002; 36:461-464
Fig. 1. A
Fig. 1. Selective angiography of the right thyrocervical trunk shows a pseudoaneurysm(arrow) from a branch of the right thyrocervical trunk.
Fig. 1. B
Fig. 1. Selective angiography of the right thyrocervical trunk shows a pseudoaneurysm(arrow) from a branch of the right thyrocervical trunk.
Fig. 2. A
Fig. 2. On post-embolization angiography, the right thyrocervical trunk was successfully embolized and the pseudoaneurysm was not visualized. The embolization was done using nine of microcoils and one vial of glue(arrow head).
Fig. 2. B
Fig. 2. On post-embolization angiography, the right thyrocervical trunk was successfully embolized and the pseudoaneurysm was not visualized. The embolization was done using nine of microcoils and one vial of glue(arrow head).
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by