중심단어
Hepatocellular carcinoma; hepatic arteries, chemotherapeutic embolization; cerebral infarction
임상소견
간세포암으로 간우엽절제술 및 고주파열소작술, TACE 시행 받았던 환자로 재발 간세포암에 대한 7번째 TACE 위해 내원함. 7번째 TACE 시술 4시간 후 좌측 상하지 motor weakness 발생하였음.
진단명
Cerebral embolism following TACE
영상소견
TACE 시술 전 CT 영상에서 간좌엽에 다수의 lipiodol uptaken nodule들이 있고 여러 군데 tumor들에 lipiodol defect area가 있어 잔류 간세포암이 의심되었음.
시술방법 및 재료
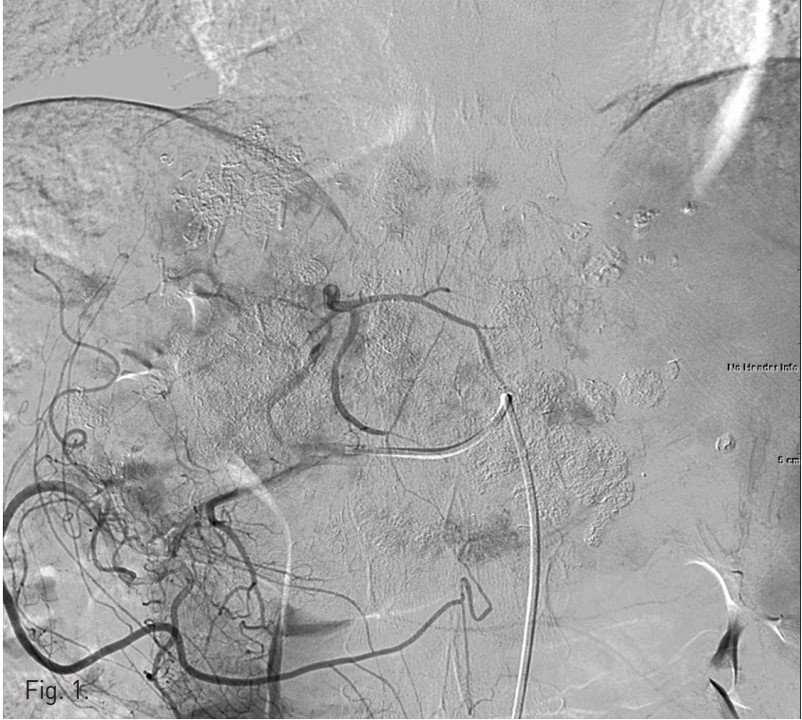
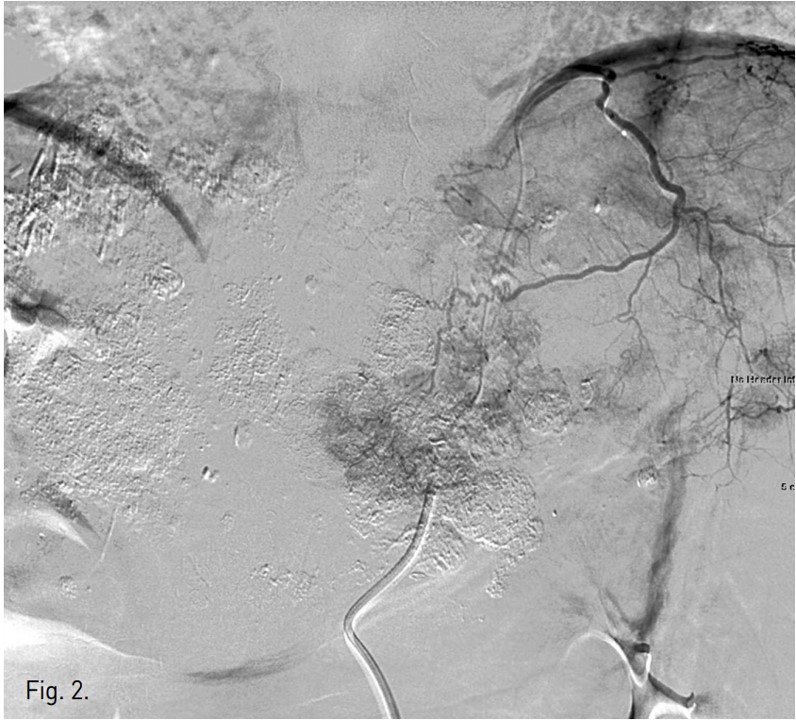
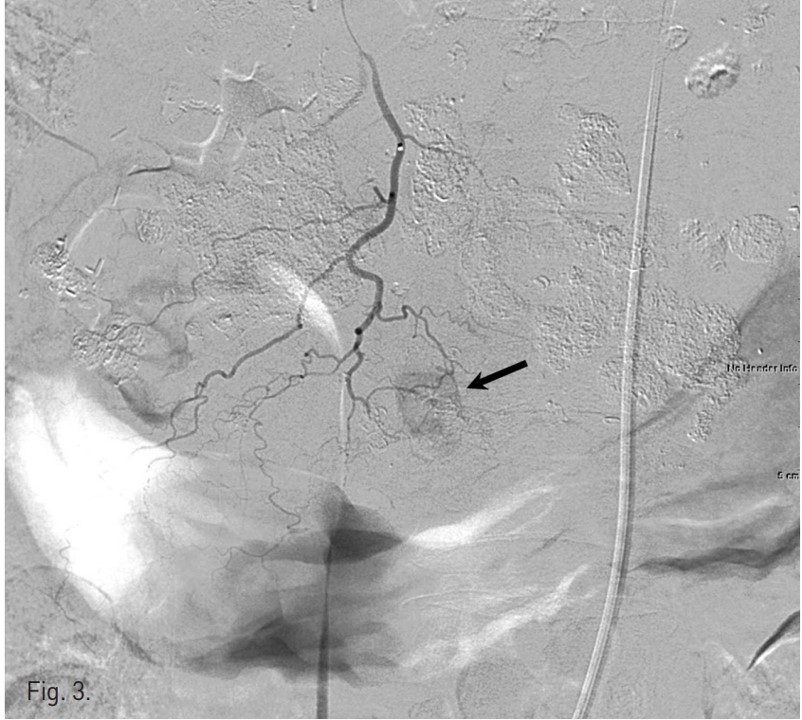
우측 대퇴동맥을 천자하여 복강동맥과 총간동맥 혈관조영술을 시행하였고 좌측 간동맥에서 혈류공급을 받는 다수의 과혈관성 종양이 관찰되었음(Fig. 1). 반복적인 TACE 후에도 CT영상에서 lipiodol defect area들이 보였기 때문에 간외측부순환에 의한 간세포암의 혈액공급 가능성이 있어 양측 횡경막하동맥과 내유방동맥 혈관조영술을 시행하였고 좌측 횡경막하동맥과 우측 내유방동맥에서 간세포암의 혈액공급이 관찰되었음(Figs. 2, 3). 이들 동맥의 혈관조영 영상에서 간정맥이나 폐혈관과의 shunt는 보이지 않았음. 2.0F 미세카테 타를 5F 카테타내 에 coaxial로 삽입하여 사용하는 동안 heparin mix 된 saline으로 카테타 flushing을 유지하였음. 각각의 간세포암 혈액 공급 혈관을 2.0F 미세카테타로 선택하여 lipiodol 13 ml와 adriamycin 60mg emulsk)n을 주입하였고,간외측부순환들은 추가적인 젤폼 색전술을 시행하였음. 색전술후 사진에서 종양내 lipiodol이 축적되고 과혈관성 종괴가 안 보이는 것을 확인한 후 시술을 마쳤음.
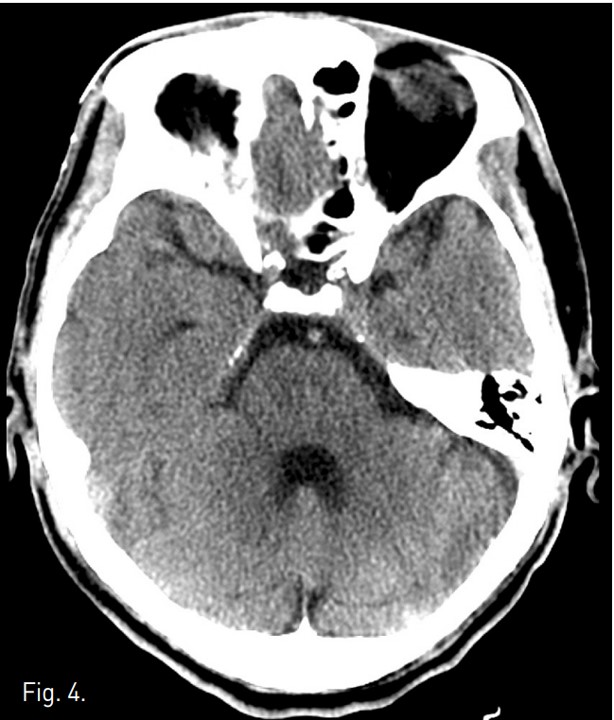
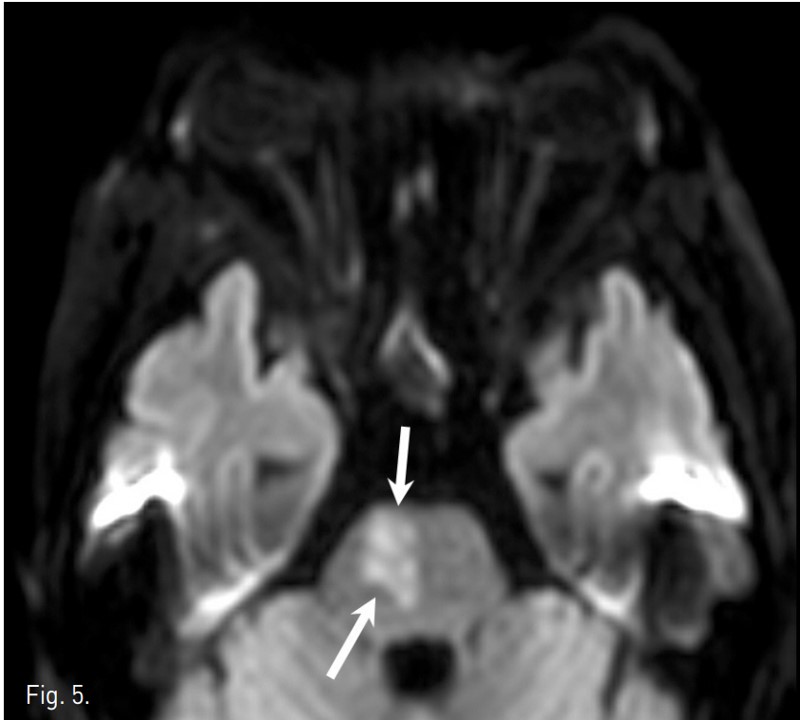
TACE 시술 4시간 후 좌측 상하지의 motor weakness와 감각 이상이 발생하였고 신경학적 검사 상 좌즉 hemiparesis와 abnormal gait pattern소견 보였음. 9시간 후 brain CT 에서 parenchymal lipiodol uptake와 같은 이상소견 발견되지 않았으나(Fig. 4), brain MRI 확산강조영상에서 상부 교뇌 우뇌 paramedian aspect와 우측 소뇌, 양측 대뇌 반구에 다발성 뇌혈관 색전증 소견이 보였음(Fig. 5). 3일 후 시행한 경식도 초음파와 contrast echocardio graphy 에서 난원공 개존 (patent foramen ovale)와 이에 의한 우좌 단락이 관찰되었음. Heparin 항응고요법 후 aspirin을 지속적으로 복용하였고, 2개월 간 재활 치료를 받은 다음 지팡이를 짚으면서 정상 보행이 가능해짐.
고찰
간세포암 치료에 널리 이용되는 TACE의 합병증으로는 간종양 또는 간 실질의 허혈성 괴사로 인한 통증, 고열, 오심 및 구토를 호소하는 색전술후 증후군이 가장 흔하며 , 패혈증/간 농양/폐렴 등의 감염 합병증과 상부위장관출혈, 담낭 경색, biloma, 급성 폐색전증, 간 부전 등이 올 수 있다.
TACE 후 뇌혈관 색전증은 현재까지 16 예 정도 보고될 정도로 매우 드문 합병증으로 보고된 증례들에서는 lipiodol이 색전증의 원인이었다. Lipiod이에 의해 뇌혈관 색전증이 발생하는 기전에는 간세포암내 동정맥 단락, 진행된 간경화환자에서 나타날 수 있는 폐내 동정맥 단락, 횡경막하동맥과 폐혈관 사이의 우좌 단락, 난원공 개존이나 심방중격 결손 등에 의한 심장내 우좌 단락 등이 있다. 간세포암내 동정맥 단락이나 횡경막하동맥과 폐혈관사이의 우좌 단락은 TACE시술을 하면서 드물지 않게 경험하기 때문에 이들 환자에서 뇌혈관 색전증의 발생 가능성을 염두에 두어야할 것이다.
Lipiodol에 의한 뇌혈관 색전증을 보고한 예들에서는 시력소실, 두통, 위약감, 의식수준의 이상 등의 증상이 나타났으며 그 중 10 예는 폐색전증에 의한 호흡기 증상이 먼저 시작되었다. 뇌혈관 색전증이 발생했던 많은 증례들에서 15-20 ml 이상의 lipiodol이 사용되었지만, 그 이하의 양을 사용했음에도 뇌혈관 색전증이 발생했던 증례들도 있어 다량의 lipiodol 사용이 뇌혈관 색전증 발생과 연관되는지에 대해서는 보다 많은 증례 연구가 필요한 실정이다.
기존 증례들에서는 간동맥이나 횡경막하동맥 등에서만 색전술을 시행하였기 때문에 lipiodol이 뇌혈관 색전증의 원인으로 쉽게 추정되었지만, 본 증례는 TACE시술 동안 양측 내유방동맥 혈관조영술을 시행하면서 뇌혈관 주변에서의 직접적인 카테타 조작이 있었기 때문에 lipiodol뿐만 아니라 카테타에서 발생된 혈전도 뇌혈관 색전증의 원인으로 고려될 수 있다.
Lipiod이이 원인이 되는 경우 non-contrast CT에서 lipiodol에 의한 high density가 색전부위에 보이는 데 반해 본 증례의 CT영상에서 이상소견이 없었던 점을 고려하면 본 증례에서는 lipiodol보다는 혈전에 의해 뇌혈관 색전증이 발생된 것으로 추정된다. 본 증례에서는 혈전발생을 줄이고자 heparinized saline으로 카테타 flushing을 했음에도 혈전이 발생한 것으로 여겨지며, TACE시술 동안 내유방동맥 혈관조영술이 필요한 경우 혈전에 의한 뇌혈관 색전증이 발생할 수 있다는 점을 주의하고 혈전발생을 최소화시키기 위한 노력이 요망된다.
참고문헌
1. Wu L, Yang VF, Liang J, et al. Cerebral lipiodol embolism following transcatheter arteriaI chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma. World J Gastroenterol 2010; 16:398-402
2. Chung RJ, Park SY, Kim YI, et al. Cerebral Lipiodol Embolism after Transcatheter ArteriaI Chemoembolization of Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Korean J Gastroenterol 2009; 54:130-134
3. Zhao H, Wang HQ, Fan QQ, et al Rare pulmonary and cerebral complications after transarterial chemoembolization for hepatocellular carcinoma: A case report. World J Gastroenterol 2008; 14:6 425-6427
4. Sakamoto I, Aso N, Nagaoki K, et al. Complications associated with transcatheter arterial embolization for hepatic tumors. Radiographics 1998;18:605-619
5. Yoo KM, Yoo BG, Kim KS, et al Cerebral lipiodol embolism during transcatheter arterial chemoembolization. Neurology 2004; 63:181-183
Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Common hepatic arteriogram shows multiple hypervascular tumor stainings in the remnant left hepatic lobe.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. Left inferior phrenic arteriogram shows multiple hypervascular tumor stainings in the left lateral segment.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 3. Right internal thoracic arteriogram shows a hypervascular tumor staining in segment 4(arrow).
Fig. 4.
Fig. 4. Pre-contrast brain CT scan at the level of the upper pons demonstrates no abnormality.
Fig. 5.
Fig. 5. Diffusion weighted image of brain MRI demonstrates a wedge shaped lesion with high signal intensity in the right paramedian aspect of the upper pons(arrows).
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by