중심단어
Isolated dissection, dissecting aneurysm, mesenteric artery, stent, coil
임상소견
1개월 전 급성복통으로 내원하여 시행한 복부 CT상 상장간막동맥에 벽내혈종이 관찰되어 보존적 치료 후 임상 호전되어 퇴원하였던 환자로, 추적 복부 CTA상 벽내혈종의 진행과 박리성동맥류가 발생하여 치료가 의뢰되었다.
진단명
Dissecting aneurysm of SMA
영상소견
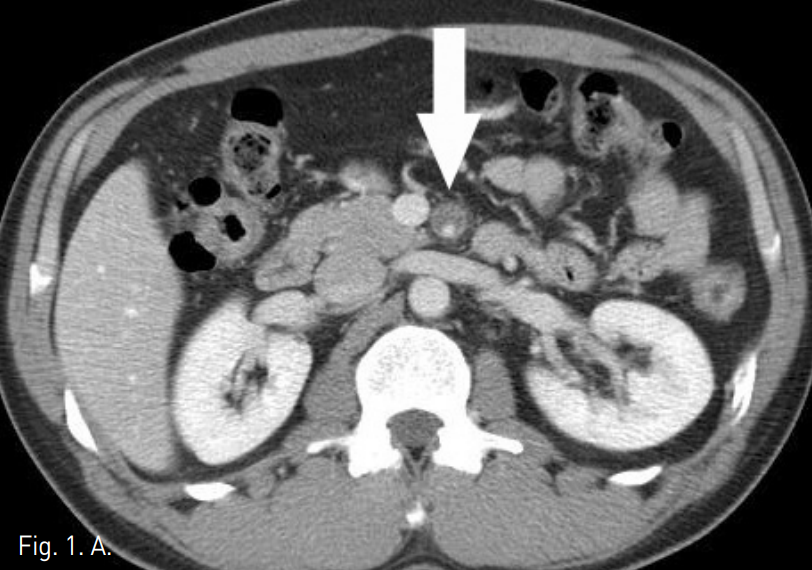
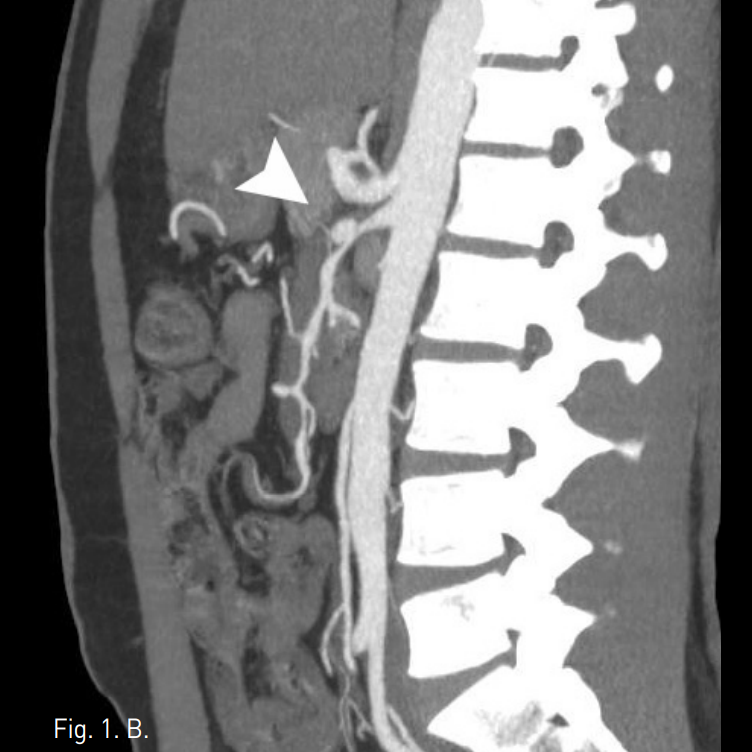
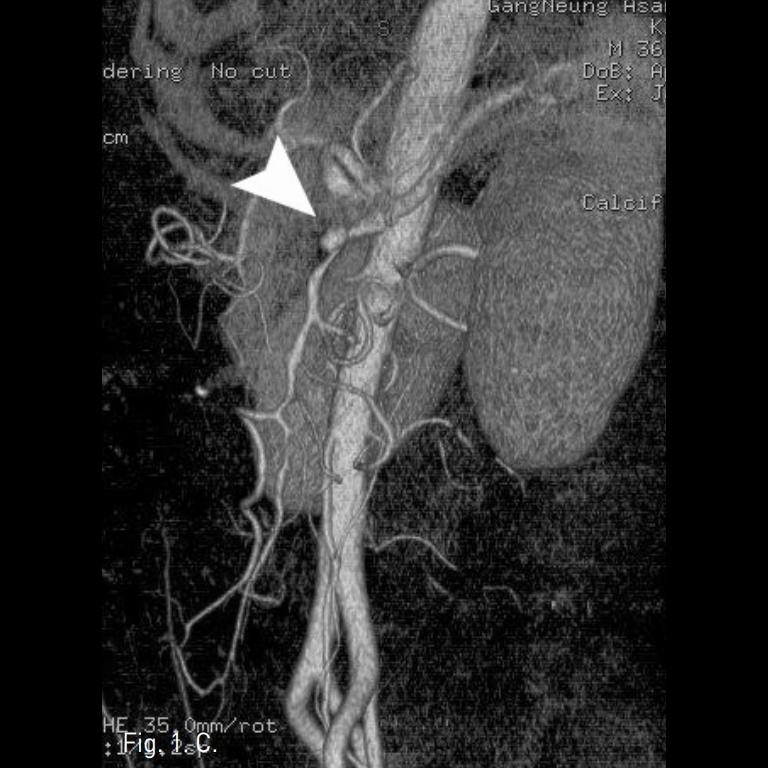
시술 전 CTA상 상장간막동맥 근위부에 직경 10mm 크기의 박리성동맥류가 확인되었고, 상장간막동맥은 벽내혈종으로 인해 혈관 직경은 12mm로 커지고 내강은 3mm로 협착소견을 보였다(Fig. 1A-C).
Fig. 1
A-C. Initial CT scan (A) shows dilated SMA with circumferential intramural hematoma and stenotic true lumen (arrow). Sagittal reconstructed MIP image (B) and volume rendered 3D CTA (C) show 1cm sized dissecting aneurysm (arrow hed) at proximal SMA and diffuse narrowing of true lumen.
시술방법 및 재료
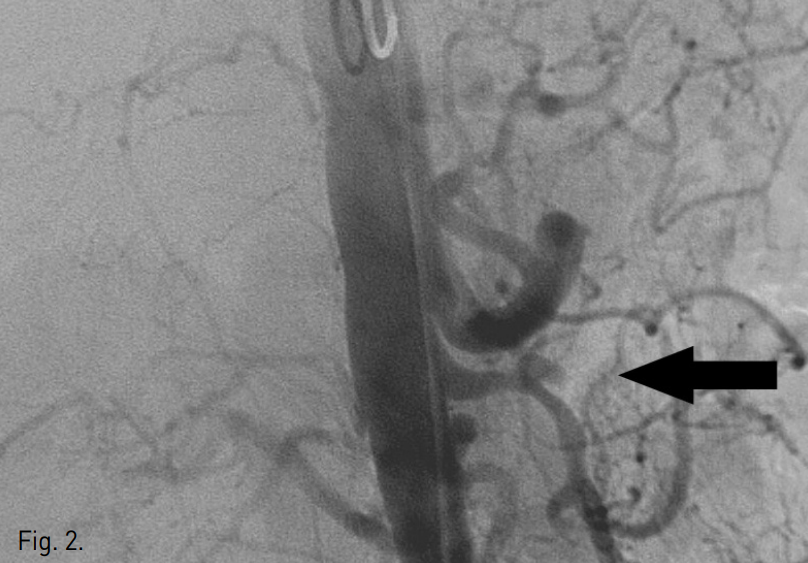
우측 대퇴동맥에 5F sheath (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)를 삽입 후 5F pig-tail catheter (Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA)로 복부대동맥조영술을 시행하였다. 대동맥조영술상 상장간막동맥 근위부에 dissecting aneurysm이 관찰되었고 상장간막동맥은 patent하였으나 intramural hematoma로 인해 luminal narrowing 소견을 보였다(Fig. 2).
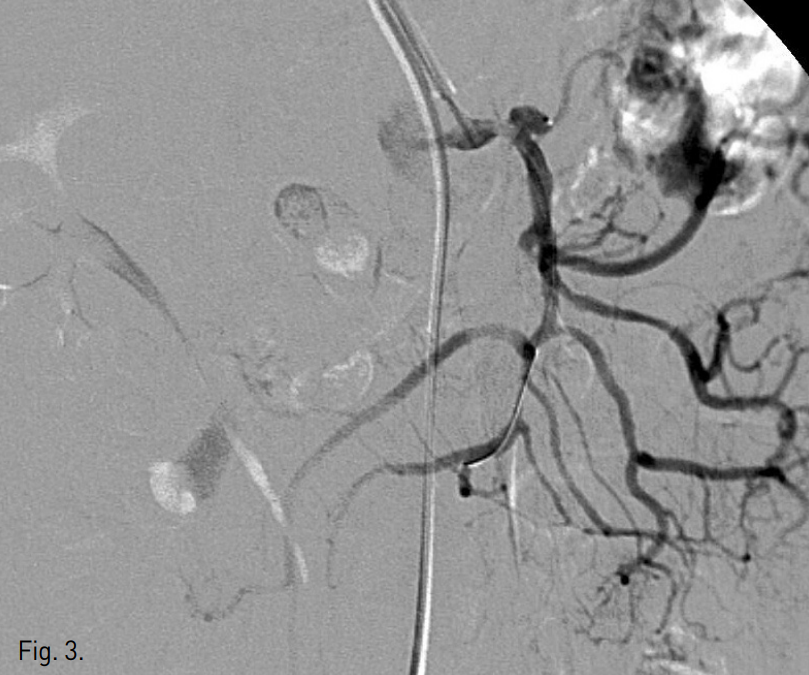
5F Yashiro catheter (Glide catheter, Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)로 상장간막동맥을 selection 후 2.5F microcatheter (Renegade, Boston scientific, Cork, Ireland)와 0.014 inch microwire (Transend EX soft tip, Boston scientific, Miami, FL, USA)를 사용하여 dissecting aneurysm을 먼저 selection하여 aneurysm내에 microcatheter를 거치하였다(Fig. 3).
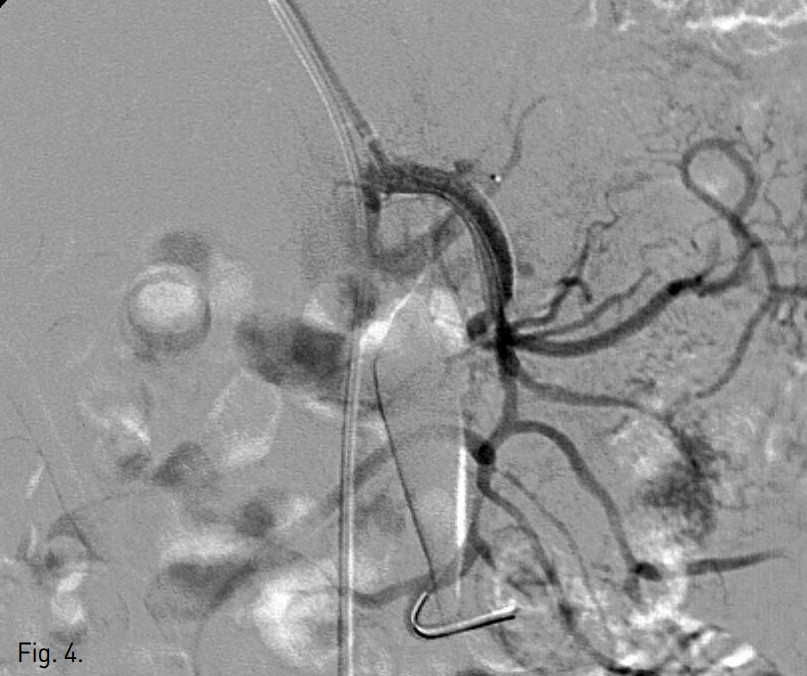
이어서 초음파 유도 하에 우측 상완동맥을 micropuncture introducer set (Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA)으로 access 후 6F sheath(Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)를 거치하고, 6F multipurpose guiding catheter (MPA1, Cordis, Miami, FL, USA)를 사용하여 상장간막동맥 기시부에 접근하였다. 이를 통해 0.014 inch microwire를 상장간막동맥 jejunal branch까지 insertion하고, microwire를 따라 6mm x 4cm self expandable stent (Precise PRO Rx, Cordis, Miami, FL, USA)를 dissecting aneurysm 입구를 포함하여 상장간막동맥 근위부에 deploy하였다(Fig. 4).
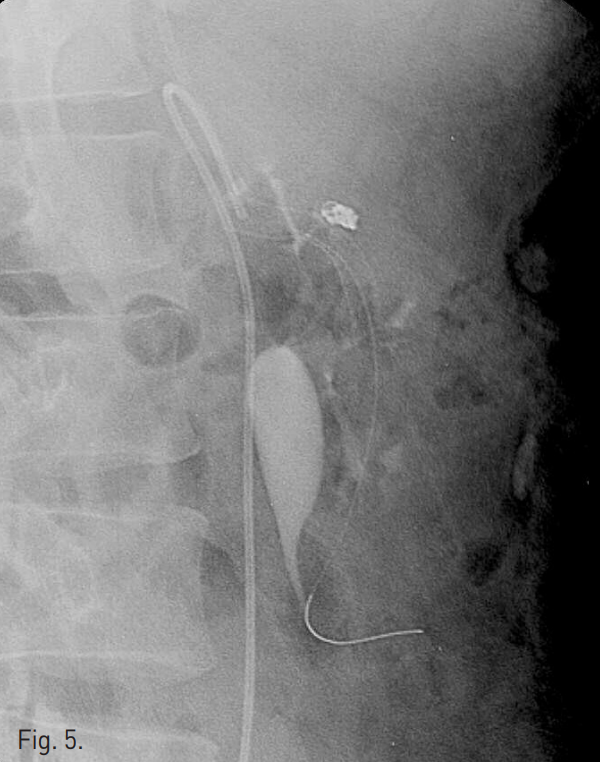
그 후 대퇴동맥을 통해 aneurysm내에 삽입했던 microcatheter를 통해 4mm x 2mm tornado microcoil (Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA) 4개를 사용하여 dissecting aneurysm 에 대한 stent assisted coil embolization을 시행하였다(Fig. 5).
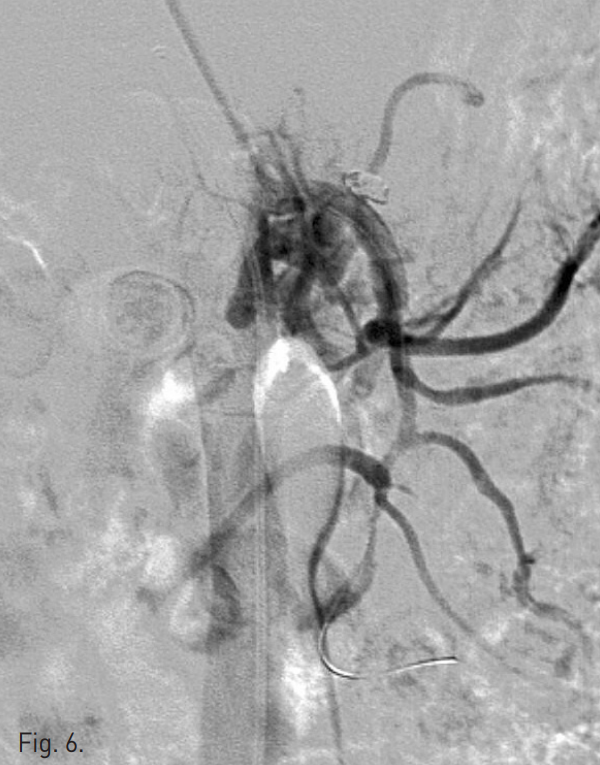
시술 후 시행한 상장간막동맥조영술상 dissecting aneurysm은 폐색되었고 상장간막동맥의 flow는 잘 유지되었다(Fig. 6). 시술 1주 후 시행한 CTA상 상장간막동맥의 벽내혈종은 그 양이 감소하였고, luminal narrowing은 호전되었으며, 동반된 합병증은 없었다(Fig. 7A, B).
Fig. 2
Abdominal aortogram reveals a dissecting aneurysm (arrow) at proximal SMA and irregular luminal narrowing of SMA
Fig. 3
Selection of dissecting aneurysm was performed using a microcatheter.
Fig. 4
A 6mm x 4cm self-expandable nitinol stent was placed in the true lumen of proximal SMA. The neck of dissecting aneurysm was fully covered by the stent.
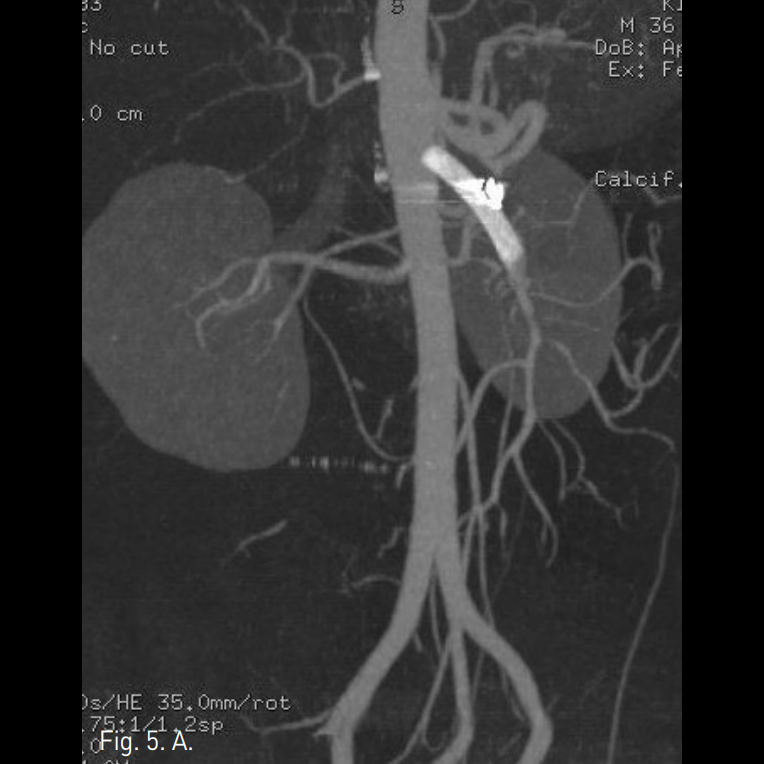
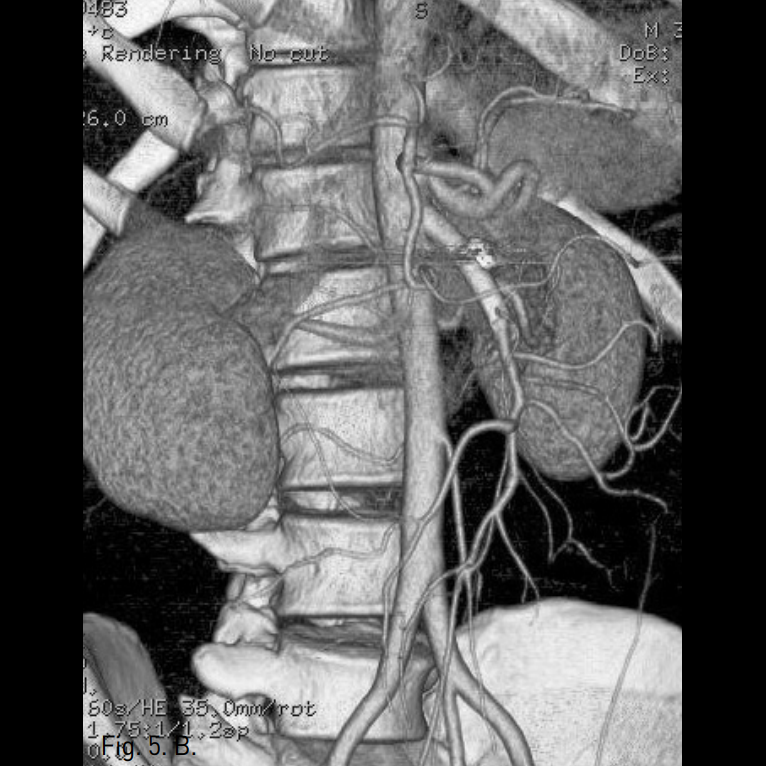
Fig. 5
A radiograph taken after stent assisted coil embolization of dissecting aneurysm demonstrates coil packed aneurysm sac.
Fig. 6
Immediately after intervention, SMA angiogram shows a good patent true lumen and ner completely embolized dissecting aneurysm.
Fig. 7
A, B. Oblique sagittal reconstructed MIP image (A) and volume rendered 3D CTA (B) obtained 1 week after procedure reveal patent SMA with decreased intramural hematoma and no residual filling of contrast media at the embolized aneurysm.
고찰
상장간막동맥에 발생하는 자발성 단독 박리(isolated spontaneous dissection of SMA)는 흔치 않은 질환으로 주로 40세 이상의 남자에서 발생하며, 증상이 없는 경우도 있으나 대개 급성복통을 유발하고, 심하면 상장간막동맥 폐쇄 및 혈전색전증으로 인한 복막염증상이나 저혈량성 쇽을 유발할 수도 있다. 가능한 발생 원인은 낭성동맥근층괴사(cystic medial necrosis), 섬유근성 이형성증(fibromuscular dysplasia), 죽종동맥경화증(atherosclerosis), 고혈압(hypertension) 등이 있으나, 보고 된 바에 의하면 상기 원인과 관련이 없는 경우가 많고 따라서 정확한 원인은 아직 밝혀지지 않은 상태이다.
진단은 CT scan에서 내막판(intimal flap)이나 벽재혈전증(mural thrombosis), 그리고 박리성동맥류(dissecting aneurysm)를 확인하면 가능하나, 이들 견이 늘 보이는 것은 아니므로 상장간막동맥 직경이 커지거나 동맥 주위 지방층의 음영증가 소견이 보이면 감별진단에 포함시켜야 한다. 혈관조영술상 박리소견은 double lumen, dissection flap, eccentric stenosis가 있으며, 혈관조영술은 박리의 범위, 재진입 혈류유무, 상장간막동맥의 전장 평가가 가능하고 바로 혈관 내 치료를 시행할 수 있는 장점이 있다.
치료는 mesenteric ischemia로 인해 bowel necrosis가 의심되는 경우 수술적 치료가 필요하고, 급성복통만 있거나 증상이 없는 경우 혈관 내 치료나 보존적 관찰을 할 수 있다. 그러나 보존적 관찰의 경우 40%에 이르는 실패율로 인해 근래에는 혈관 내 치료를 선호 한다. 혈관 내 치료는 혈관 박리 부위에 자가팽창형 금속스텐트를 설치하거나, 피복스텐트를 설치할 수 있고, 재진입혈류의 존재, 가강에서 기시하는 가지혈관으로 인해 가강이 막히지 않거나 박리성 동맥류로 인해 혈관파열의 가능성이 있는 경우 코일 색전술을 추가로 시행할 수 있다. 이때 사용하는 금속 스텐트는 minimal shortening, good conformability, and flexibility 특성이 있어야 하고 장관의 운동에도 위치 이동이 없어야 한다.
References
1. Ozaki T, Kimura M, Yoshimura N et al Encovascular treatment of spontaneous isolated dissecting aneurysm of the superior mesenteric artery using stent-assisted coil embolization. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2006; 29:435-437.
2. Kim JH, Rho BS Lee YH, Choi SS So BJ. Isolated spontaneous dissection of the superior mesenteric artery: Percutaneous stent placement in two patients. Korean J Radiol 2004; 5:134-138.
3. Yoon YW, Choi DH, Cho SY, Lee DY. Successful treatment of isolated spontaneous superior mesenteric artery dissection with stent placement. Cardiovasc Intervent Radiol 2003; 26:475-478.
4. Miyamoto N, Sakurai Y, Hirokami M et al. Endovascular stent placement for isolated spontaneous dissection of the superior mesenteric artery: report of a case. Radiation Medicine 2005;23:520-524.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by