중심단어
Ruptured aneurysm, bronchial artery, embolization, hemomediastinum.
임상소견
특이병력 및 외상력 없던 환자로 갑자기 발생한 흉통과 심와부 통증으로 응급실 내원함. 환자는 응급실에서 의식 저하를 보였으며, 생체징후는 혈압 120/80mmHg, 심박수 90회, 호흡수 22회였고 최초 Hb 12.3mg/dL였음. Chest radiograph에서 종격동 확장 소견이 보였고, CT angiography에서 후종격동에 조영제 유출을 동반한 거대 혈종이 관찰되었음. 환자는 8시간 뒤 혈압이 80/50mmHg로 저하되었으며, Hb 10.0mg/dL로 감소하였음.
영상소견
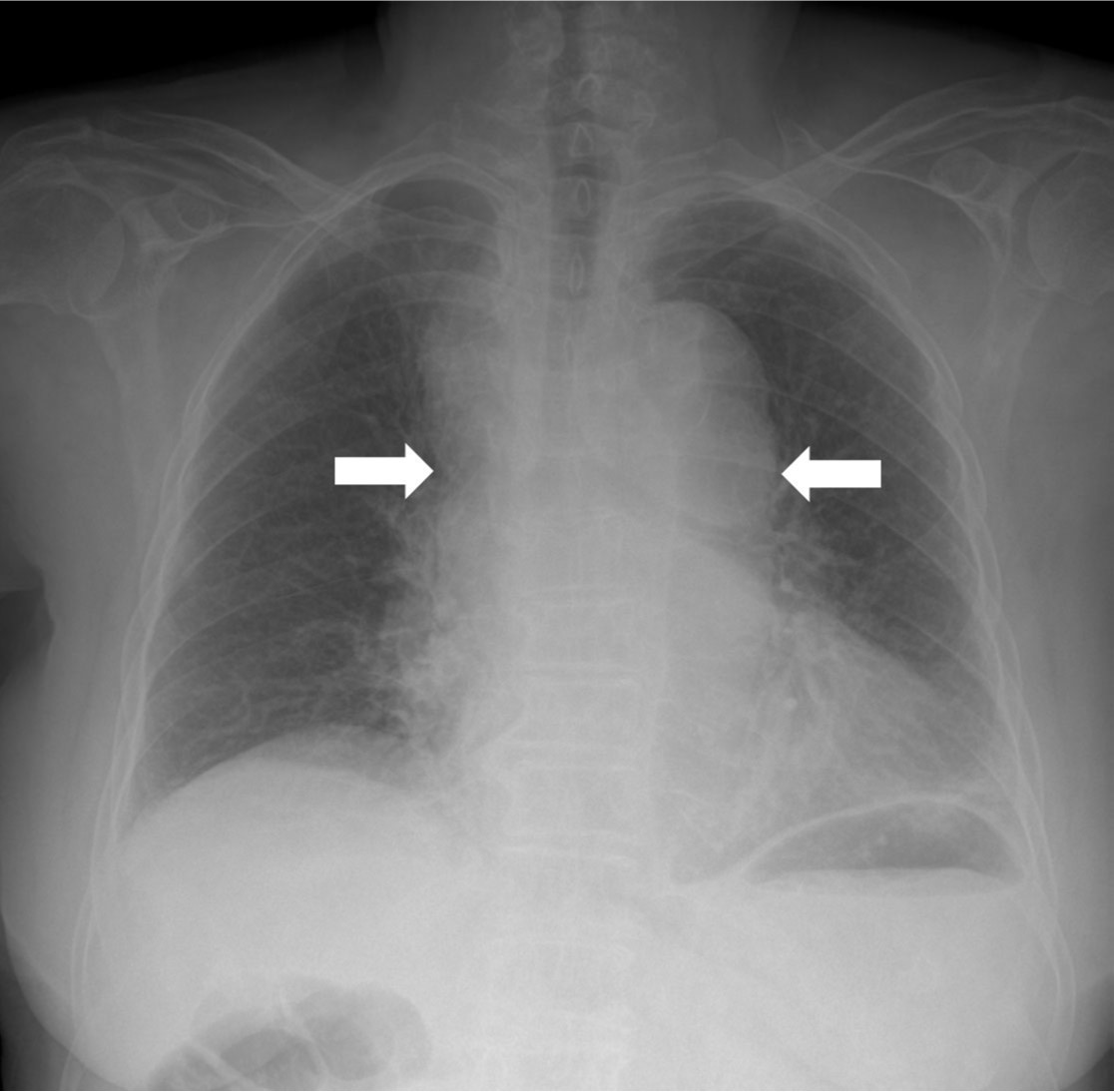
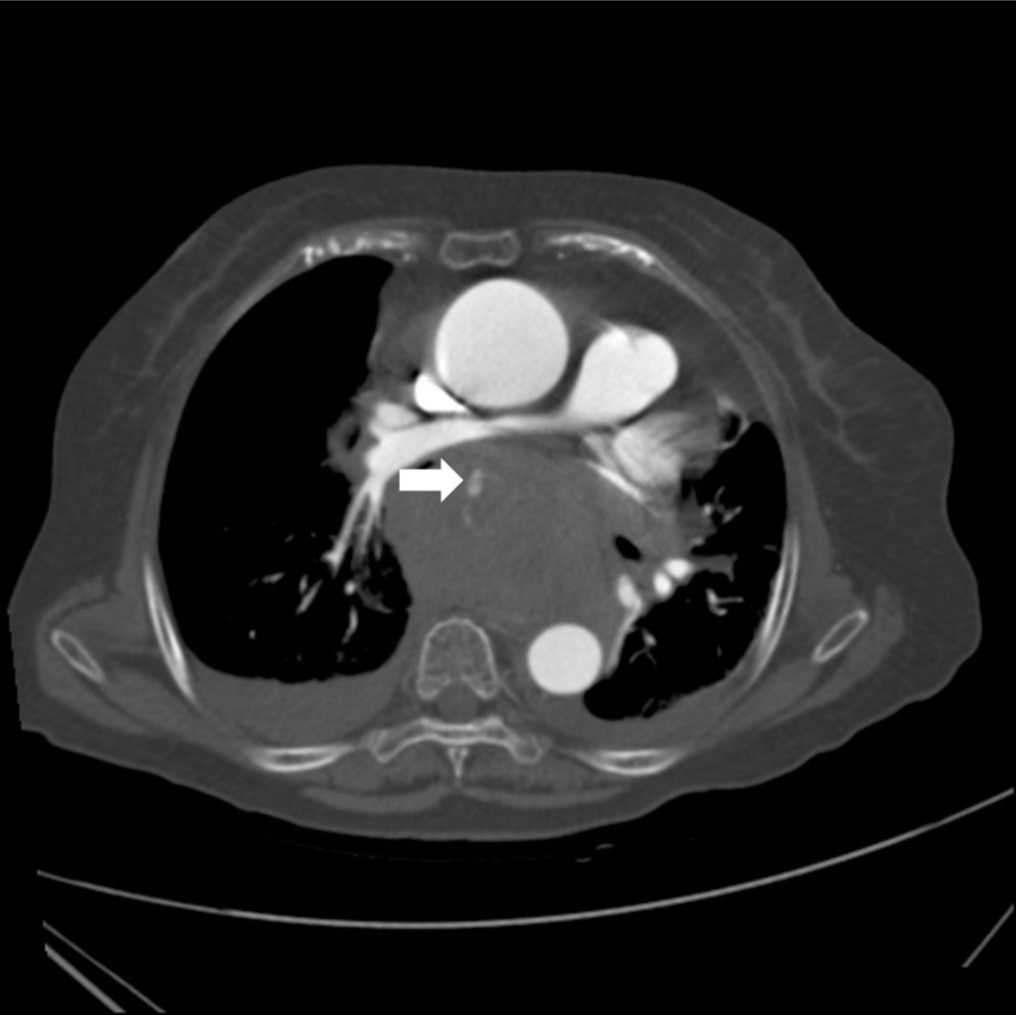
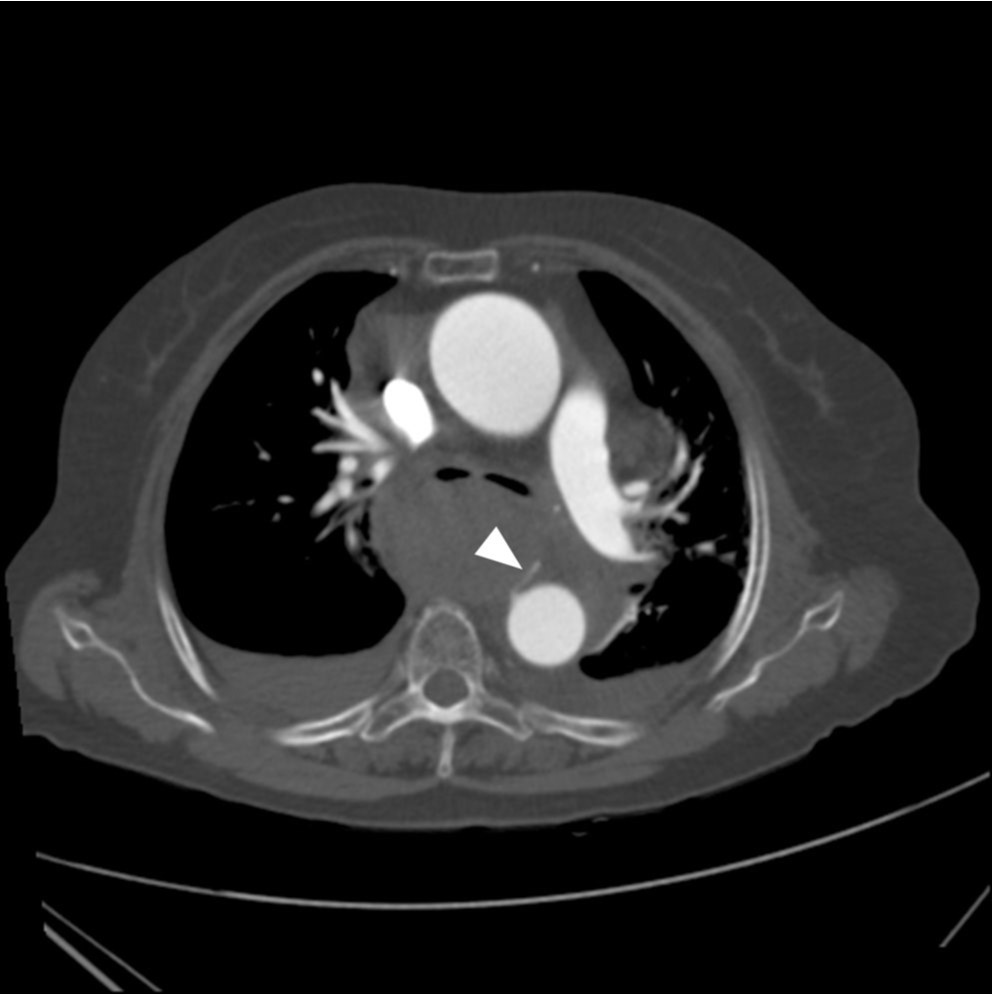
Chest radiograph에서 상부 종격동 비대를 보이고 있었고 좁아진 기관지 내강이 관찰됨(Fig. 1). CT angiography에서 후종격동에 거대한 혈종이 있으며, 이 혈종 내부로 조영제가 유출되고 있음(Fig. 2A). 조영제 유출은 하행 대동맥에서 기시하는 우기관지동맥과 연결됨(Fig. 2B).
시술방법 및 재료
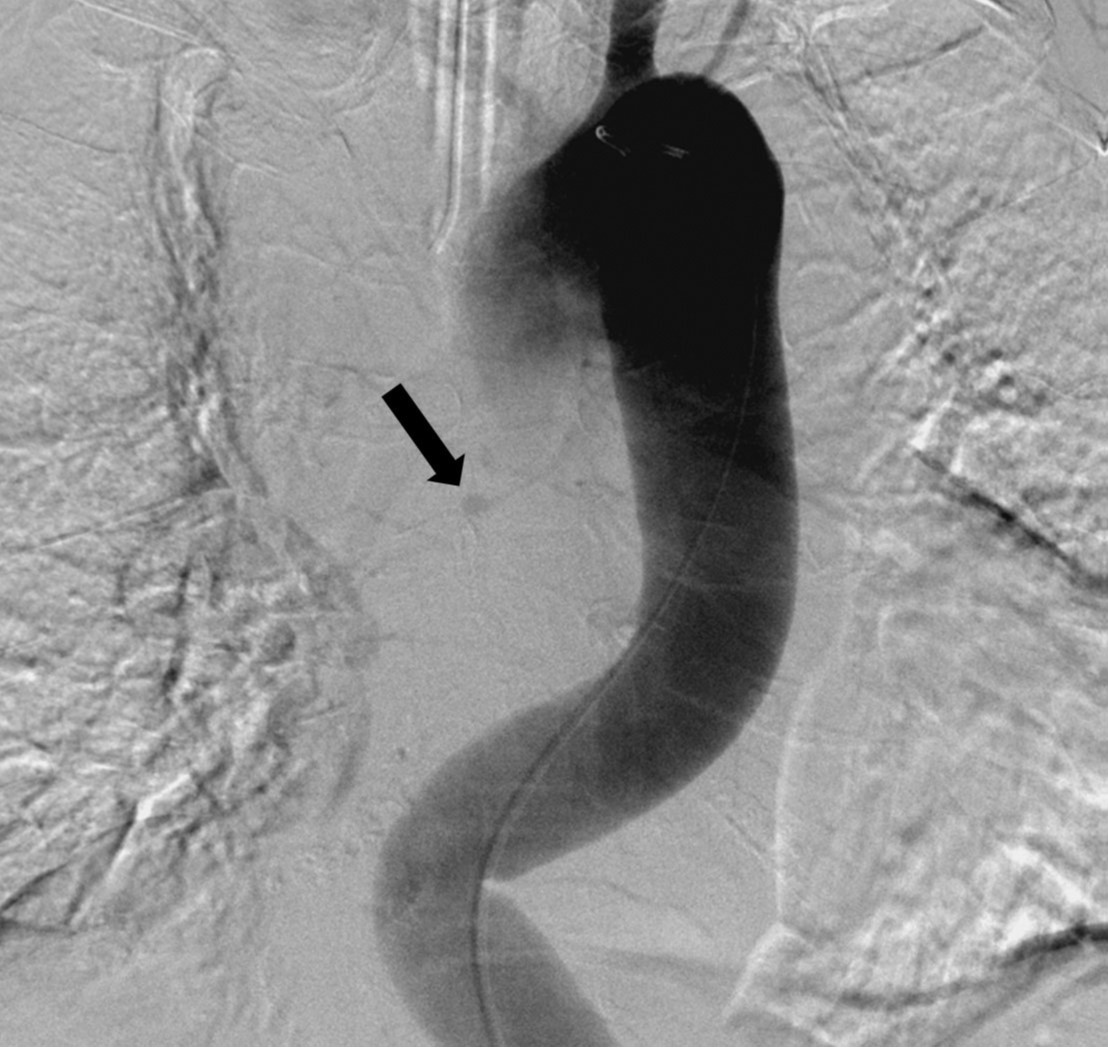
우총대퇴동맥을 통해 5F sheath를 삽입하였다. 5F flush catheter를 대동맥궁에 위치시켜 대동맥조영술을 시행하였고, 대동맥조영술에서 흉부 정중앙에 둥근 모양의 동맥류로 추정되는 병소가 관찰되었음(Fig. 3A). 5F bronchial catheter를 이용해 선택적 우기관지동맥조영술을 시행하였고, 우기관지동맥의 중간 부분에 위치한 동맥류를 확인할 수 있었음(Fig. 3B). 2.0F Progreat microcatheter(Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)를 이용하여 우기관지동맥 동맥류의 원위부까지 진입하였고, 총 9개의 3mm x 2cm Tornado coil(Cook, Bloomington, USA)을 이용하여, 동맥류의 원위부부터 근위부까지 색전을 시행하였다. 색전술 중 동맥류로 추정되는 병소로부터 조영제 유출이 있었고, 코일의 일부가 파열된 동맥류로 돌출하는 것을 볼 수 있었다(Fig. 4). 이후 우기관지동맥의 근위부에서 gelfoam을 이용하여 추가로 색전술을 시행하였다. 이후 시행한 선택적 우기관지동맥조영술 및 대동맥조영술에서 동맥류의 완전 차단과 더 이상의 조영제 유출이 없는 것을 확인하였다(Fig. 5)
환자는 시술 1시간 후 거대 혈종으로 인한 좌심방 압전으로 인해 다시 혈압 저하가 발생하여 흉강경을 이용한 종격동 혈종제거술 및 감압술을 시행하였다. 2주일 뒤 시행한 조영증강 흉부 CT에서 종격동에 존재했던 혈종은 거의 흡수되었으며(Fig. 6), 환자는 시술 19일 후 정상 활동 가능한 상태로 퇴원하였다.
고찰
급성 종격동 혈종은 주로 흉부 외상이나 대동맥 파열, 척추동맥 박리, 혹은 종양이나 수술, 혈관조영술, 약제 등에 의해 발생되는 것으로 알려져 있다(1,2). 기관지동맥의 파열은 종격동 출혈의 아주 드문 원인으로 알려져 있으며, 기관지 동맥류도 선택적 기관지동맥조영술을 시행한 환자의 1%에서만 발견되는 드문 질환이다(3). 기관지 동맥류의 원인은 잘 알려져 있지 않으나, 기관지동맥 혈류 증가, 선천적 동맥류 형성, 기관지 확장증, 규폐증, 결핵, 무기폐, 외상 등이 알려지고 있다(3-7).
파열 전까지는 대개 증상이 없으나(8) 종격동 내의 동맥류는 급성 상대정맥 폐색, 연하곤란, 혈흉, 종격동 혈종, 토혈을 일으킬 수 있다(9). 본 환자는 특별한 기저질환이 없어 기관지 동맥류의 발생 및 파열의 원인을 추정하기는 어려우며, 우기관지 동맥류가 종격동 내에 위치하였기 때문에 흔히 생각하게 되는 증상 중 하나인 객혈이 아니라 종격동 혈종 및 흉통으로 발현한 것으로 생각된다. 기관지 동맥류의 파열은 동맥류의 지름과는 관련 없는 것으로 알려져 있다(8).
기관지동맥류 파열 환자에서 혈역학적으로 안정된 경우 혈관조영술을 통해 정확한 진단 뿐만 아니라 치료적인 색전술도 시행 할 수 있다(1). 그러나 종격동 압박이나 생명을 위협할 정도의 출혈이 있는 경우에는 수술적 종격동 감압술이나 동맥류 결찰이 필요한 경우도 있다(10).
참고문헌
1. Taillé C, Fartoukh M, Houël R, Kobeiter H, Rémy P, Lemaire F. Spontaneous hemomediastinum complicating steroid- induced mediastinal lipomatosis. Chest 2001; 120:311-313.
2. Matsuge S, Hosokawa Y, Murakami Y, Satoh K. Thymoma with idiopathic thrombocytopenic purpura preceded by mediastinal hemorrhage; report of a case. Kyobu Geka 2002; 55:899-902.
3. Mizuguchi S, Inoue K, Kida A, et al. Ruptured bronchial artery aneurysm associated with bronchiectasis: a case report. Ann Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2009; 15:115-118.
4. Shaer AH, Bashist B. Computed tomography of bronchial artery aneurysm with erosion into the esophagus. J Comput Assist Tomogr 1989; 13:1069-1071.
5. Hoffmann V, Ysebaert D, De Schepper A, Colpaert C, Jorens P. Acute superior vena cava obstruction after rupture of a bronchial artery aneurysm. Chest 1996; 110:1356-1358.
6. Oka M, Fukuda M, Terashi K, et al. Bronchial artery aneurysm as a cause of atelectasis. Intern Med 1997; 36:917-919.
7. Cearlock JR, Fontaine AB, Urbaneja A, Spigos DG. Endovascular treatment of a posttraumatic bronchial artery pseudoaneurysm. J Vasc Interv Radiol 1995; 6:495-496.
8. Afksendiyos K, Gregory K, Aristotelis P, Bernard F. Ruptured mediastinal bronchial artery aneurysm: a dilemma of diagnosis and therapeutic approach. J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 1997; 114:853-856.
9. Wilson SR, Winger DI, Katz DS. CT visualization of mediastinal bronchial artery aneurysm. AJR Am J Roentgenol 2006; 187:W544-W545.
10. Seo YH, Kwak JY. Spontaneous Hemomediastinum and Hemothorax Caused by a Ruptured Bronchial Artery Aneurysm: case report. Korean J Thorac Cardiovasc Surg 2011; 44:314-317.
Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Chest radiograph shows mediastinal widening (arrows).
Fig. 2. A
Fig. 2A, B. Axial CT images reveal a large hematoma with extravasation of contrast media (arrow) in the posterior mediastinum. The extravasation was connected with the right bronchial artery (arrowhead) originated from the descending thoracic aorta.
Fig. 2. B
Fig. 2A, B. Axial CT images reveal a large hematoma with extravasation of contrast media (arrow) in the posterior mediastinum. The extravasation was connected with the right bronchial artery (arrowhead) originated from the descending thoracic aorta.
Fig. 3. A
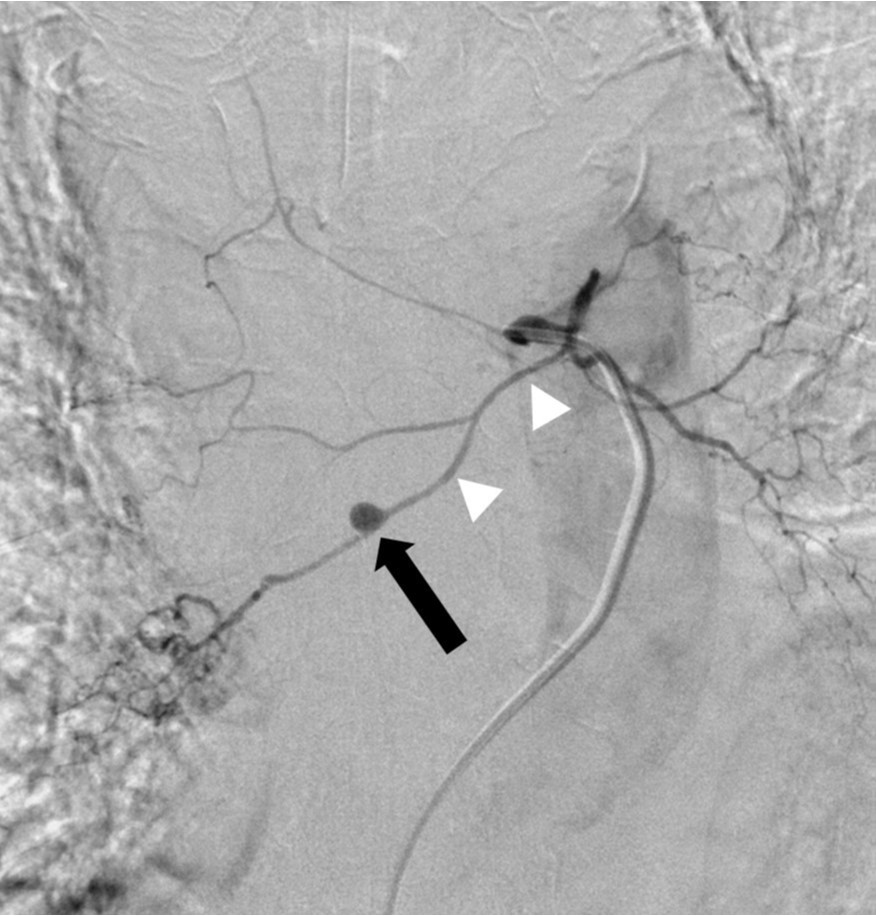
Fig. 3A, B. Thoracic aortogram (A) shows a small aneurysm (arrow) in the mid-thorax. Common bronchial arteriogram (B) reveals that the aneurysm (arrow) is located at the mid-portion of the right bronchial artery (arrowheads).
Fig. 3. B
Fig. 3A, B. Thoracic aortogram (A) shows a small aneurysm (arrow) in the mid-thorax. Common bronchial arteriogram (B) reveals that the aneurysm (arrow) is located at the mid-portion of the right bronchial artery (arrowheads).
Fig. 4.
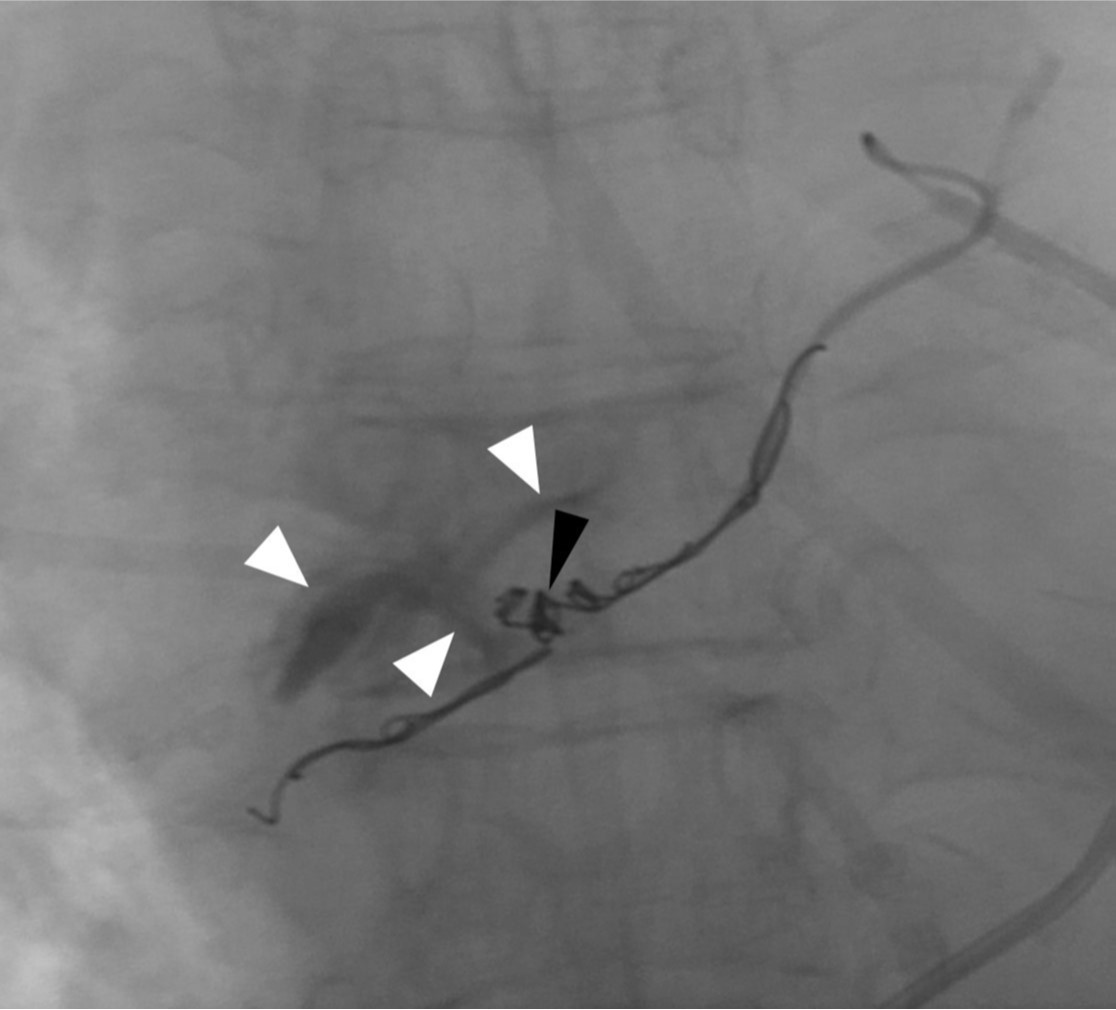
Fig. 4. Embolization of the right bronchial artery was performed using multiple coils. Note the protrusion of coils (black arrowhead) into the aneurysm sac and extravasation of the contrast media (white arrowheads) into the mediastinum.
Fig. 5.
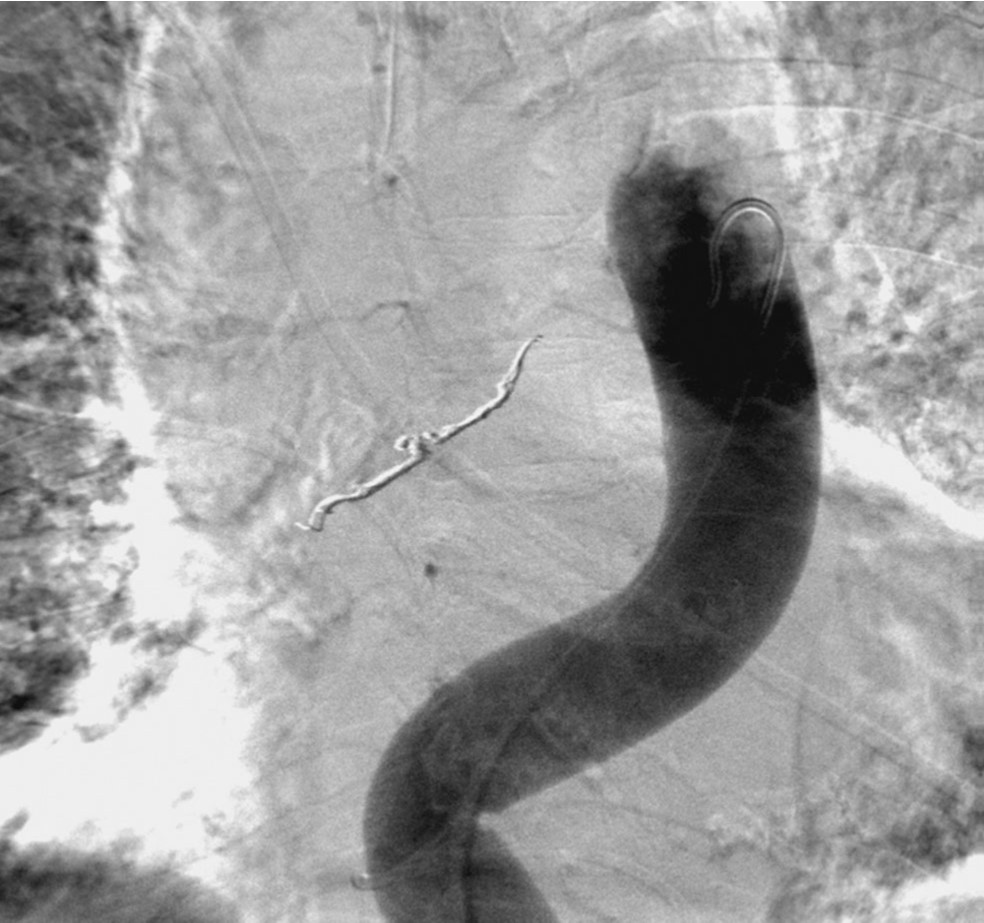
Fig. 5. The aneurysm was completely excluded and there was no more extravasation of contrast media on final thoracic aortogram.
Fig. 6.
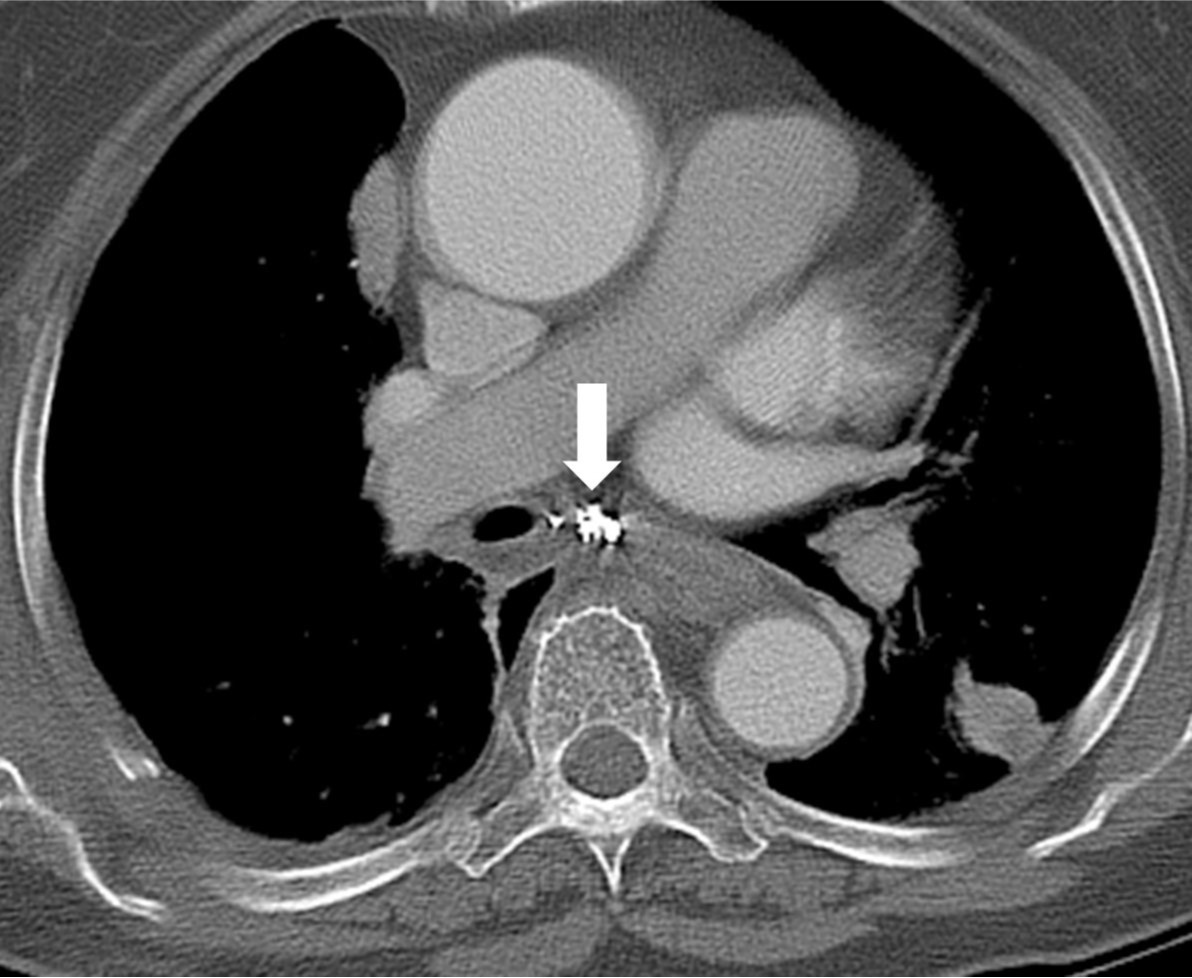
Fig. 6. On follow-up CT obtained 2 weeks after intervention, almost all hematoma in the posterior mediastinum disappears. Note the coils (arrow) in the posterior mediastinum.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by