임상소견
폐암환자로 우상엽 폐암이 주변 상부종격동과 기관, 식도주변까지 침범하고 종격동 림프절 전이를 동반하면서 얼굴부종 및 호흡곤란의 증상이 발생하였다. Superior vena cava syndrome에 대해 방사선치료를 시행한 후 2개월 경과관찰 하였으나 얼굴부종 지속되고 호흡곤란 악화되어 superior vena cava syndrome 치료위해 스텐트 삽입이 의뢰됨.
진단명
Superior vena cava syndrome
영상소견
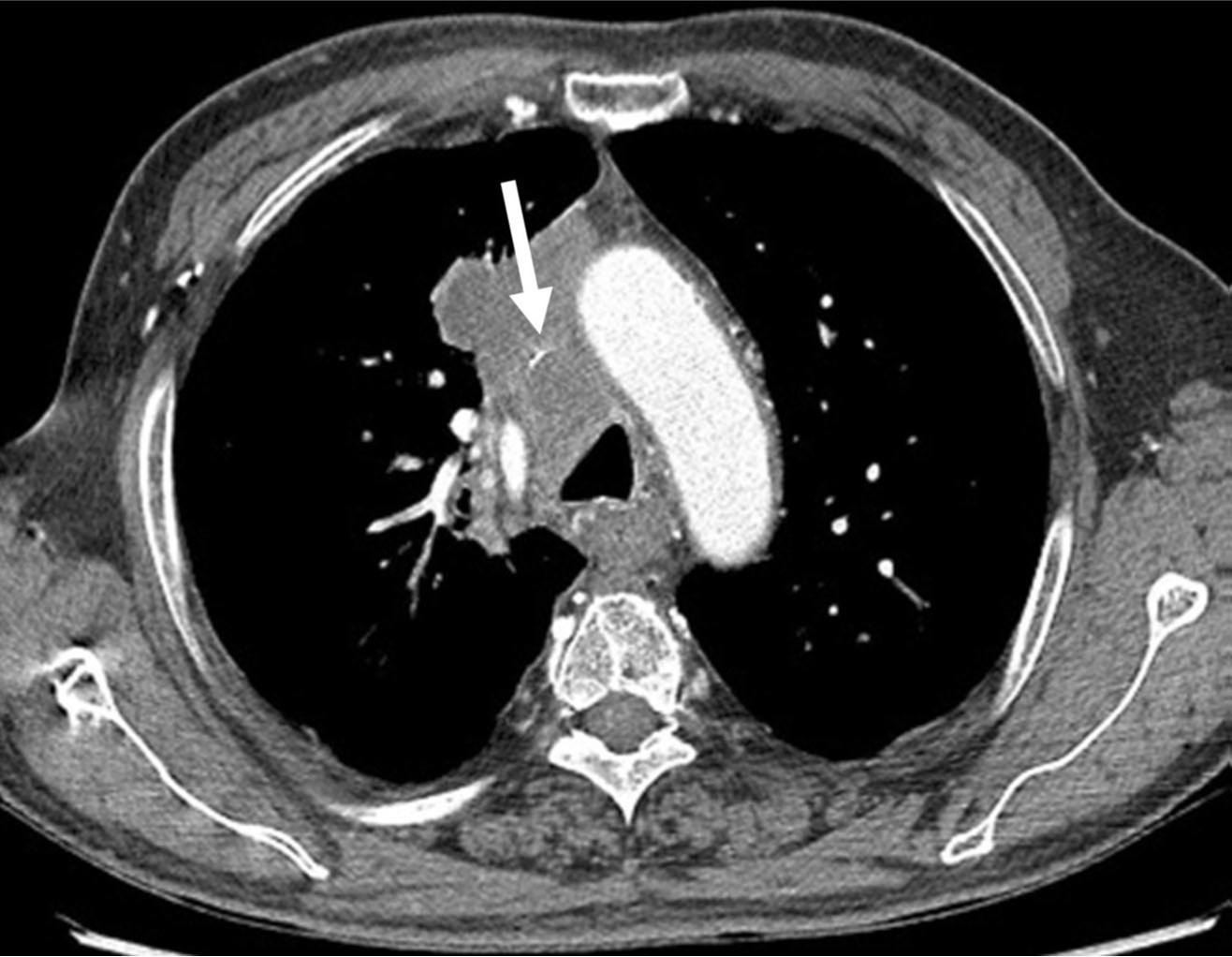
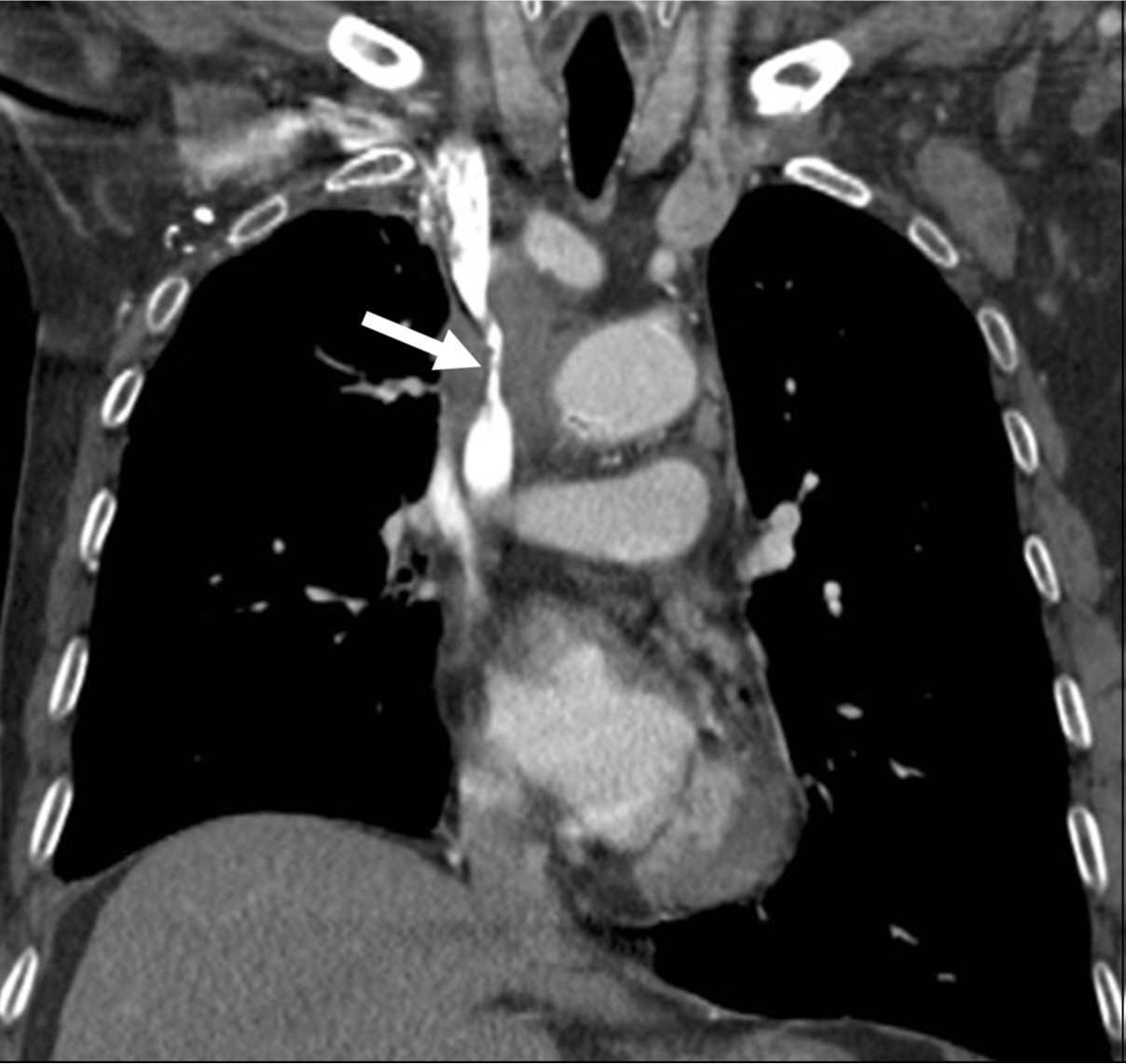
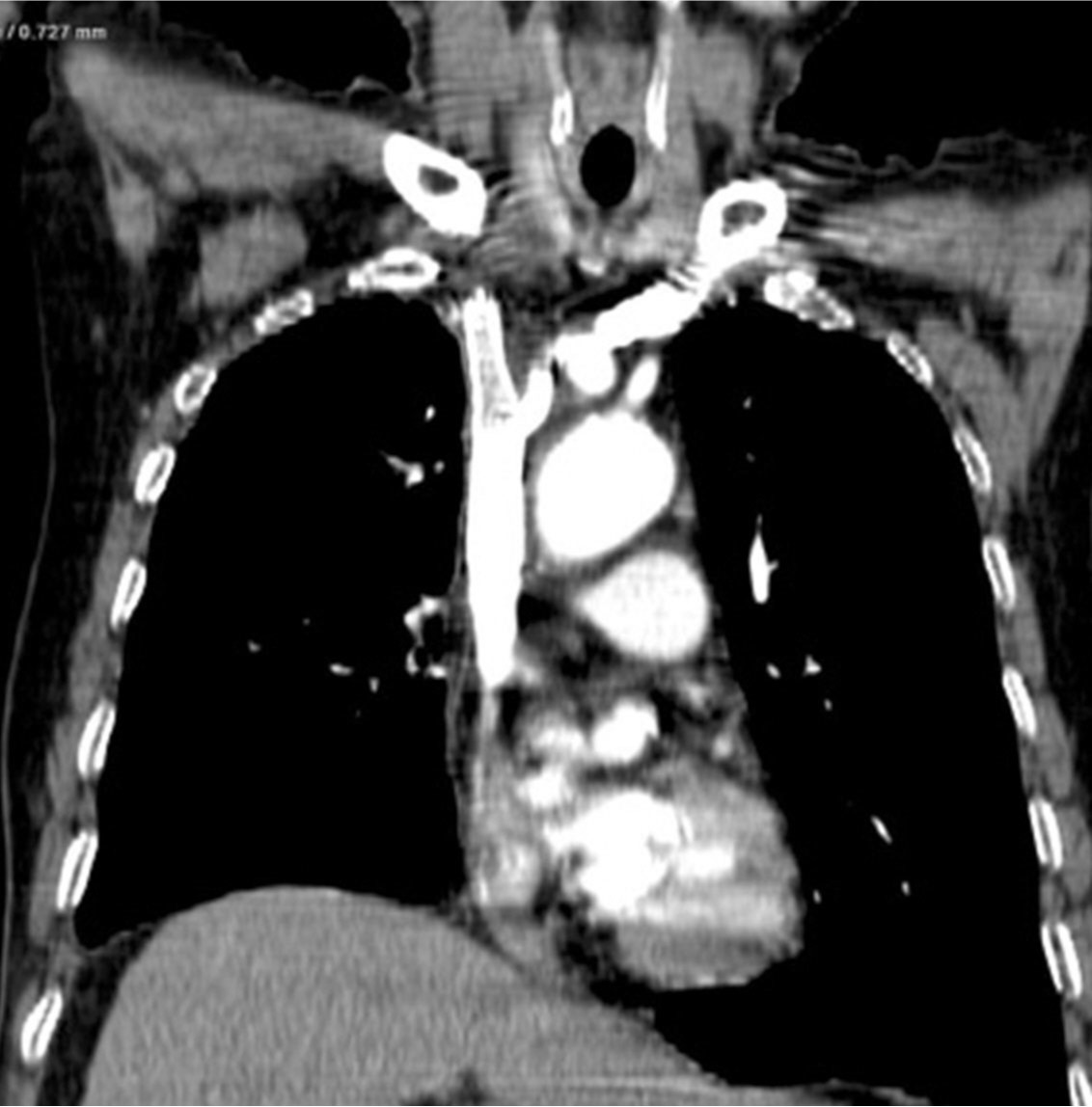
흉부 CT영상에서 폐암의 종격동 침범과 임파절 전이로 인해 상대정맥이 눌려 심하게 좁아져 있다(Fig. 1).
시술방법 및 재료
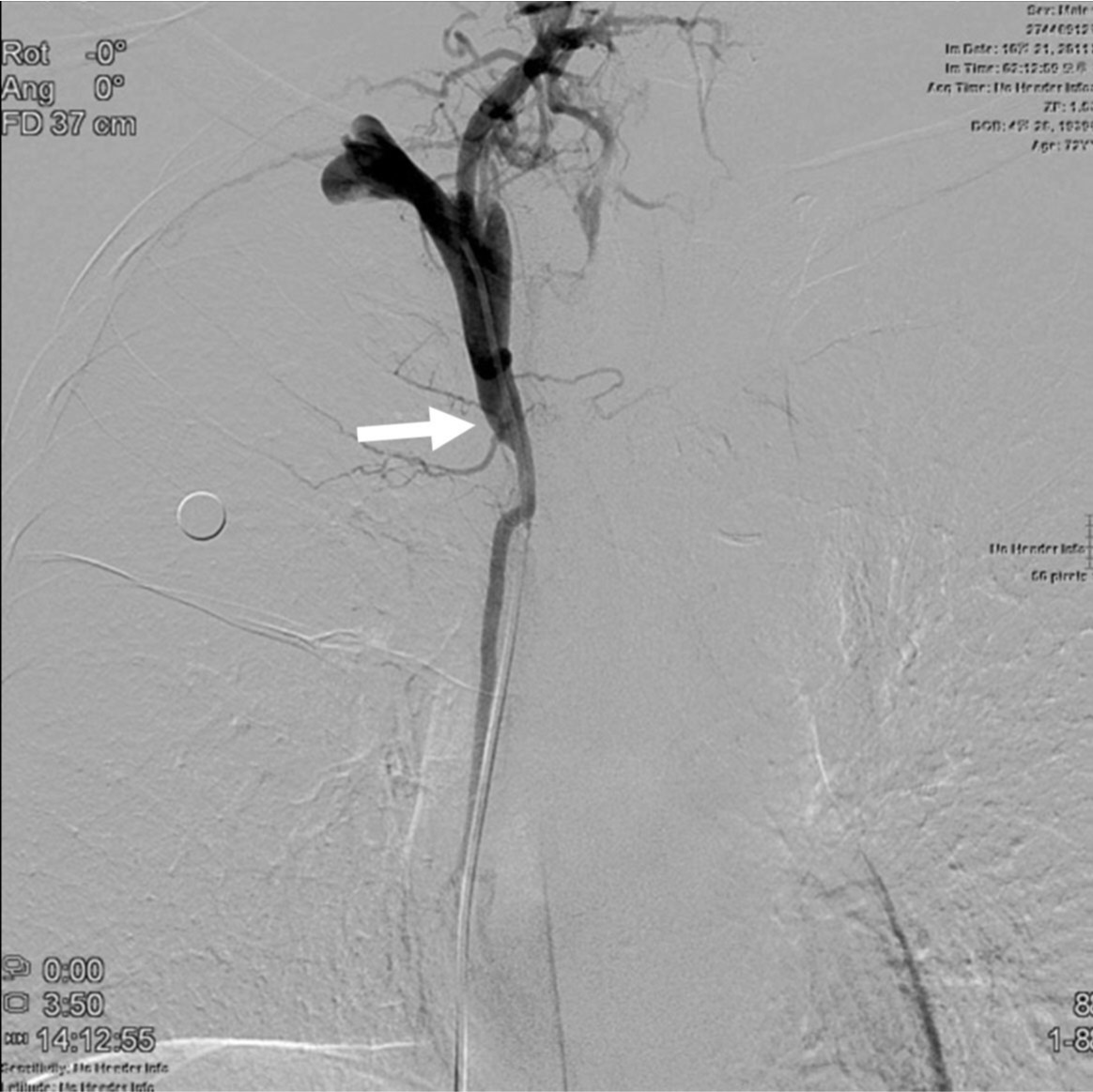
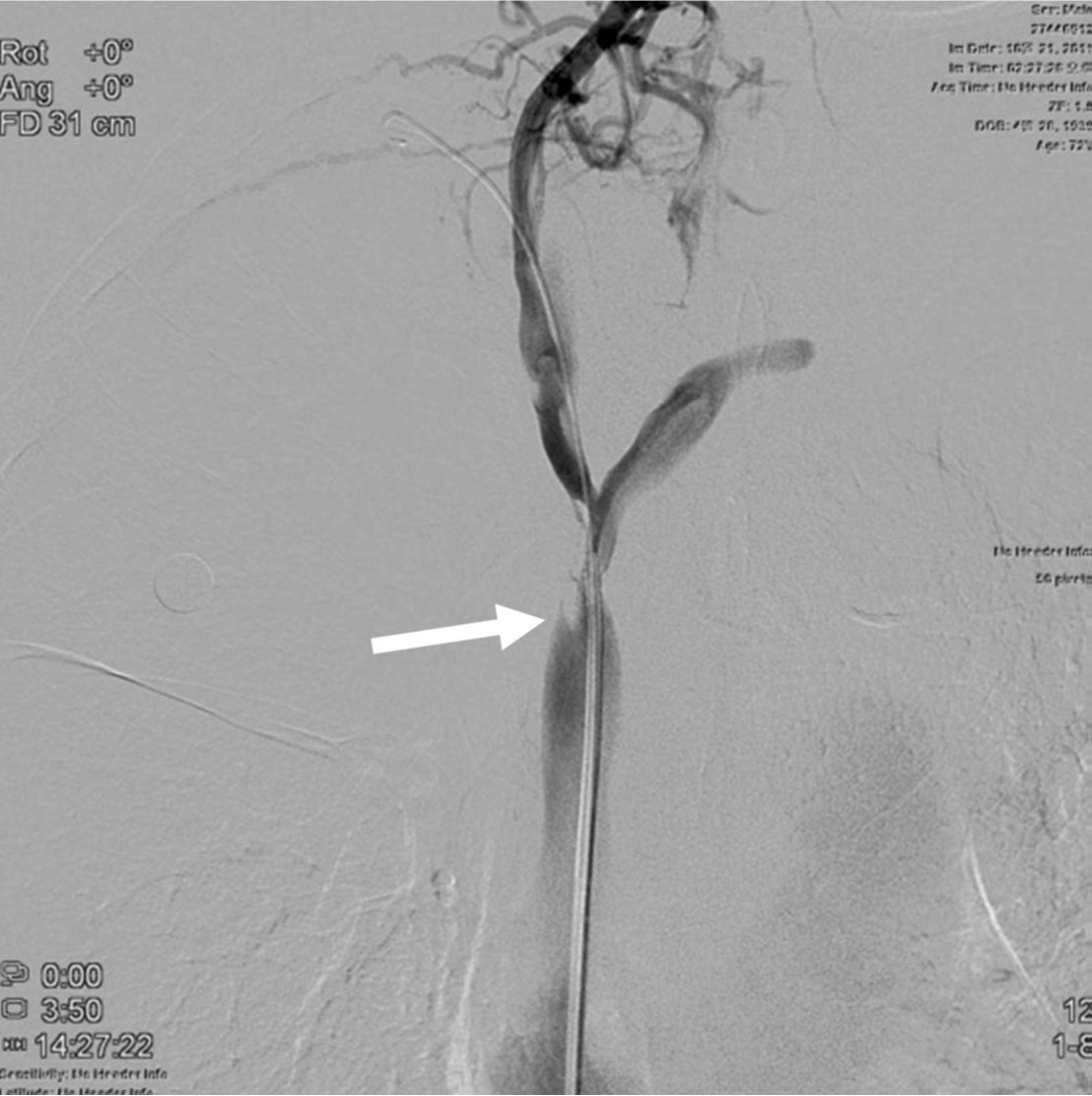
우측 대퇴정맥을 천자하여 7Fr sheath를 삽입하였고, 5Fr 카테타와 0.035-인치 유도철사를 상대정맥 근위부까지 전진한 다음 roadmap 영상하에 좁아진 상대정맥을 통과하였음. 5Fr 카테타를 우측 상완두정맥(right brachiocephalic vein)에 위치한 상태에서 시행한 정맥조영술에서 우상완두정맥 근위부에 위치한 협착 원위부 경계는 확인되었지만 심한 협착으로 인해 협착 근위부 경계는 확인이 안되었음(Fig. 2). 0.035-인치 Rosen 유도철사(Cook, Bloomington, USA)를 따라 6Fr Envoy 카테타(Cordis, Miami, USA)를 협착부위에 위치시킨 상태에서 정맥조영술을 시행하여 상대정맥에 위치한 협착 근위부 경계를 확인하였음(Fig. 3). 협착부위에 14mm x 60mm selfexpandable stent(SMART, Cordis, Miami, USA)를 설치하였고, 협착이 심하여 8mm x 40mm 풍선카테타(Synergy, Boston Scientific, Natick, USA)로 협착부위를 먼저 넓힌 다음 4mm x 40mm 풍선카테타(XXL balloon, Boston Scientific, Natick, USA)로 풍선확장술을 시행하였음(Fig. 4). 종양에 의한 협착이 심하여 풍선이 완전히 펴지지는 않았지만 풍선확장술 후 시행한 우내경정맥조영술에서 스텐트를 통해 심장으로 혈류유입이 원활하였고(Fig. 5), 우내경정맥과 스텐트 근위부 상대정맥의 혈압을 측정하였을 때 3mmHg의 혈압 차를 보여 시술을 종료하였음. 환자는 임상증상이 호전되어 시술 2일 뒤 퇴원하였고, 시술 후 6개월이 경과할 때까지 스텐트의 patency는 잘 유지되고 있었음(Fig. 6).
고찰
상대정맥증후군은 상대정맥의 폐색, 협착에 의해 생기는 symptom들과 sign들을 말하며, 몸 상부의 정맥압이 증가함에 따라 머리, 목, 팔 등에 edema, cyanosis, plethora, subcutaneous vessel들의 distension등이 나타나게 된다. 과거에는 악성질환에의한 원인이 약 90% 정도였지만, 최근에는 중심정맥 카테타나 pacemaker등의 사용빈도가 높아짐에 따라 이들에 의한 thrombosis 같은 비악성질환에 의한 원인이 약 35% 정도로 늘어났다. 가장 흔한 원인의 악성 질환은 비소세포 폐암으로 악성질환 원인의 약 50%를 차지하며, 그 외 소세포폐암(약 25%), 임파종(10%), 전이암(10%)등이 흔한 원인 악성질환이다.
상대정맥 증후군의 치료는 환자 증상의 심한 정도와 기저 악성 질환의 상태 등에 따라 결정된다. 흔히 사용되는 치료법은 방사선치료로 상대정맥 증후군을 일으키는 대부분의 tumor type들은 방사선치료에 sensitive한 것으로 알려져 있다. 치료성적은 방사선치료 2주 후 소세포폐암 환자의 78%, 비소세포폐암 환자의 63%에서 증상의 완전 소실을 경험하며, 특히 첫 72시간 내 뚜렷한 호전이 나타나는 것으로 보고되고 있다. 비호지킨 임파종과 소세포폐암 환자의 80%, 비소세포폐암의 40%는 전신 항암치료에 반응하며 방사선 치료와 동등한 효과를 나타내는 것으로 보고되었다. 스텐트 삽입술도 상대정맥 증후군의 한 치료방법이 될 수 있는데 악성 종양의 조직형을 모르는 경우에도 효과를 기대할 수 있고, mesothelioma 같이 항암치료나 방사선치료에 반응하지 않는 경우에도 효과적이며 호흡곤란과 같이 심한 증상이 있는 경우 즉각적인 효과를 기대할 수 있다. Cyanosis와 같은 증상은 대개 수시간 내 호전되는 것으로 알려져 있으며, edema는 48-72시간 이내에 개선된다. 스텐트 삽입 후 합병증은 3-7%정도로, infection, pulmonary embolus, stent migration, insertion sitehematoma, bleeding, 그리고 아주 드물게 perforation등이 있다.
참고문헌
1. Wilson LD, Detterbeck FC, Yahalom J. Superior vena cava syndrome with malignant causes. N Engl J Med 2007;356:1862-1869.
2. Rowell NP, Gleeson FV. Steroids, radiotherapy, chemotherapy and stents for superior vena caval obstruction in carcinoma of the bronchus: a systematic review. Clinical Oncology 2002;14:338-351.
3. Kee ST, Kinoshita L, Razavi MK, Nyman UR, Semba CP, Dake MD. Superior vena cava syndrome: treatment with catheter-directed thrombolysis and endovascular stent placement. Radiology 1998;206:187-193.
4. Anderson PR, Coia LR. Fractionation and outcomes with palliative radiation therapy. Semin Radiat Oncol 2000;10:191-199
Fig. 1. A
Fig. 1A, 1B. The axial (A) and coronal (B) images of chest CT scans show segmental severe narrowing(arrows) of the superior vena cava resulting from compression by the surrounding malignant tumor with mediastinal lymph node metastasis.
Fig. 1. B
Fig. 1A, 1B. The axial (A) and coronal (B) images of chest CT scans show segmental severe narrowing(arrows) of the superior vena cava resulting from compression by the surrounding malignant tumor with mediastinal lymph node metastasis.
Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. On right brachiocephalic venogram, the distal end(arrow) of the stenosis is only seen with no visualization of its proximal end.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 3. Venogram obtained with injection of the contrast media at the stenosis clearly shows the proximal end(arrow) of the stenosis.
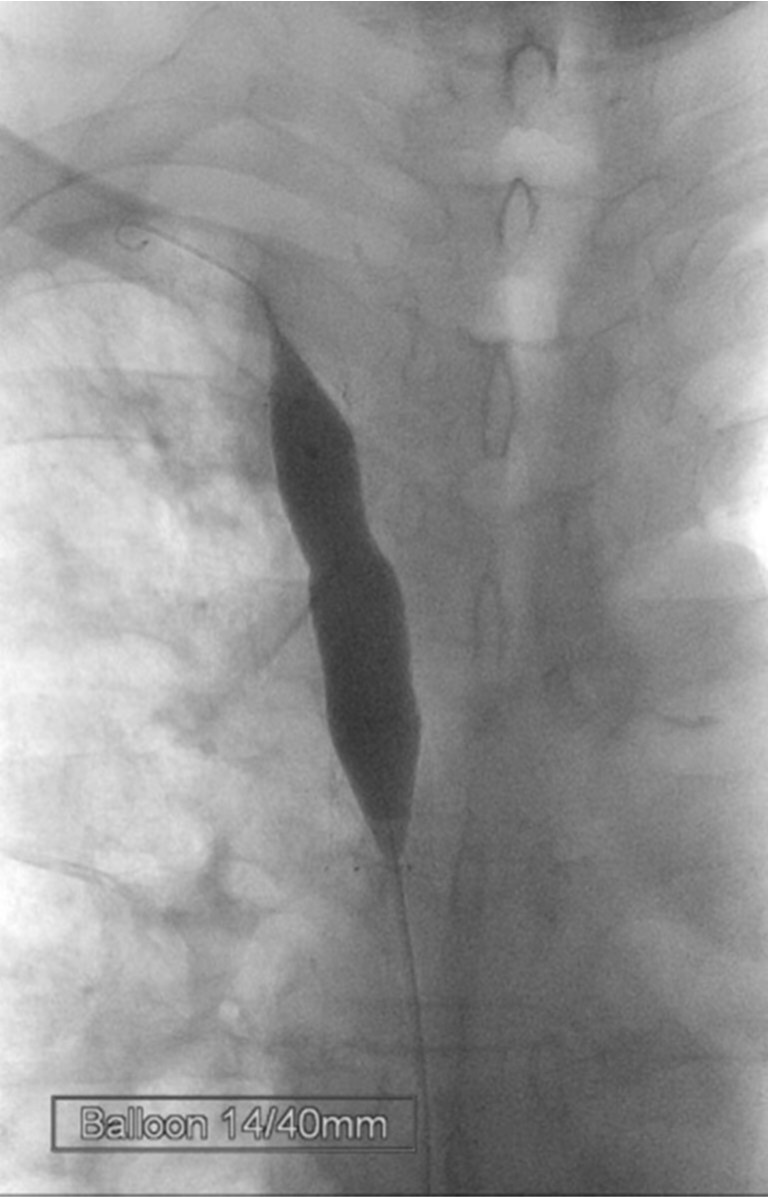
Fig. 4.
Fig. 4. After placing the self-expanding stent, the stenotic segment was dilated with a balloon catheter.
Fig. 5.
Fig. 5. Right internal jugular venogram demonstrates good venous return through the stent into the heart.
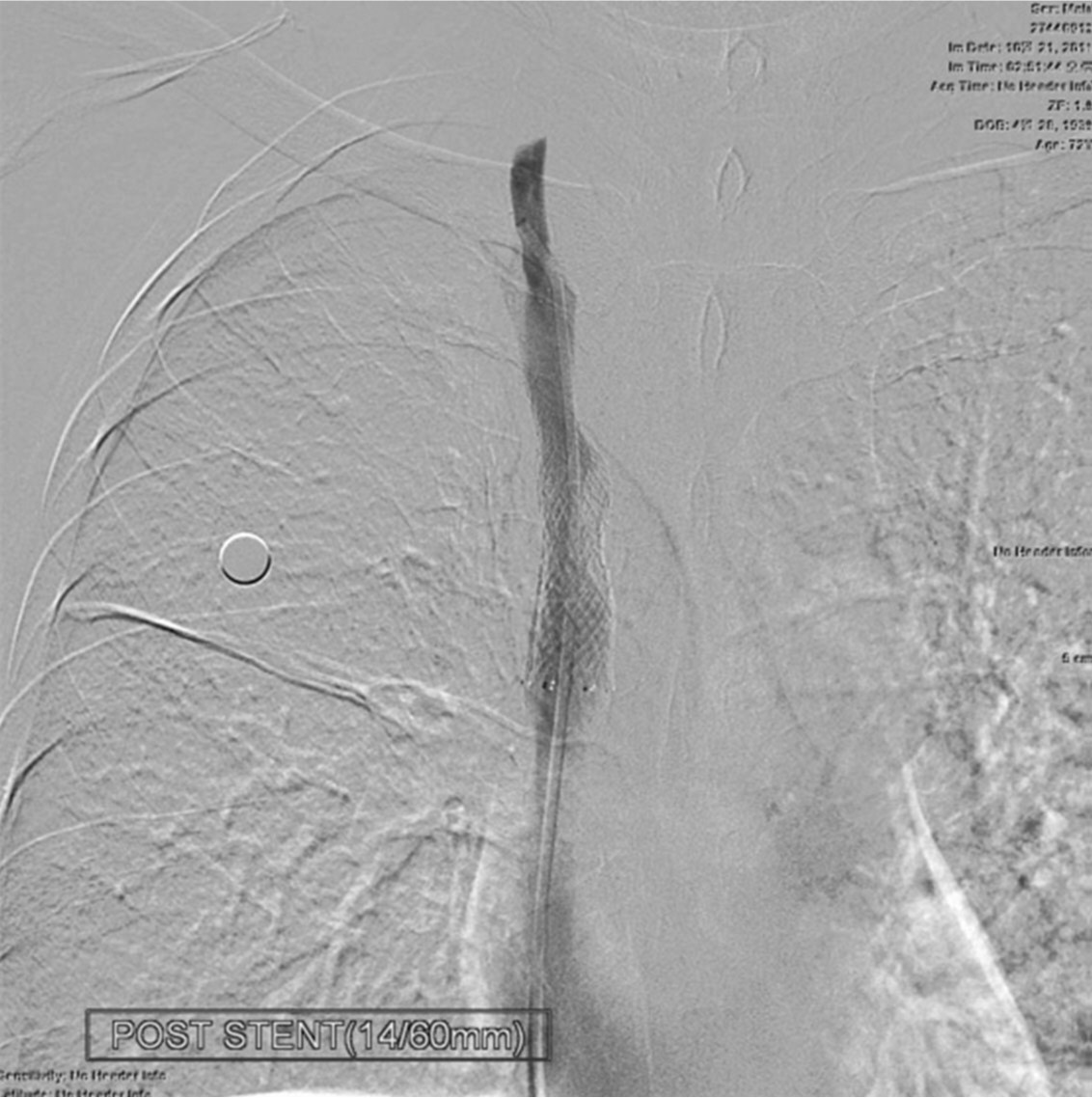
Fig. 6.
Fig. 6. Until 6-month follow-up with CT scan, the patency of the stent placed in the superior vena cava is well preserved.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by