중심단어
Living donor liver transplantation, TIPS, Budd-Chiari syndrome, thrombectomy
임상소견
생체간이식 수술 1년 후 만성 거부반응으로 인한 문맥압항진증으로 난치성 복수와 식도정맥류 출혈이 발생하여 TIPS를 시행 받았음. TIPS 6일 후 빌리루빈 수치가 시술 전 1.8 mg/dl에서 10 mg/dl로 증가하였음.
진단명
Acute Budd-Chiari syndrome after TIPS
영상소견
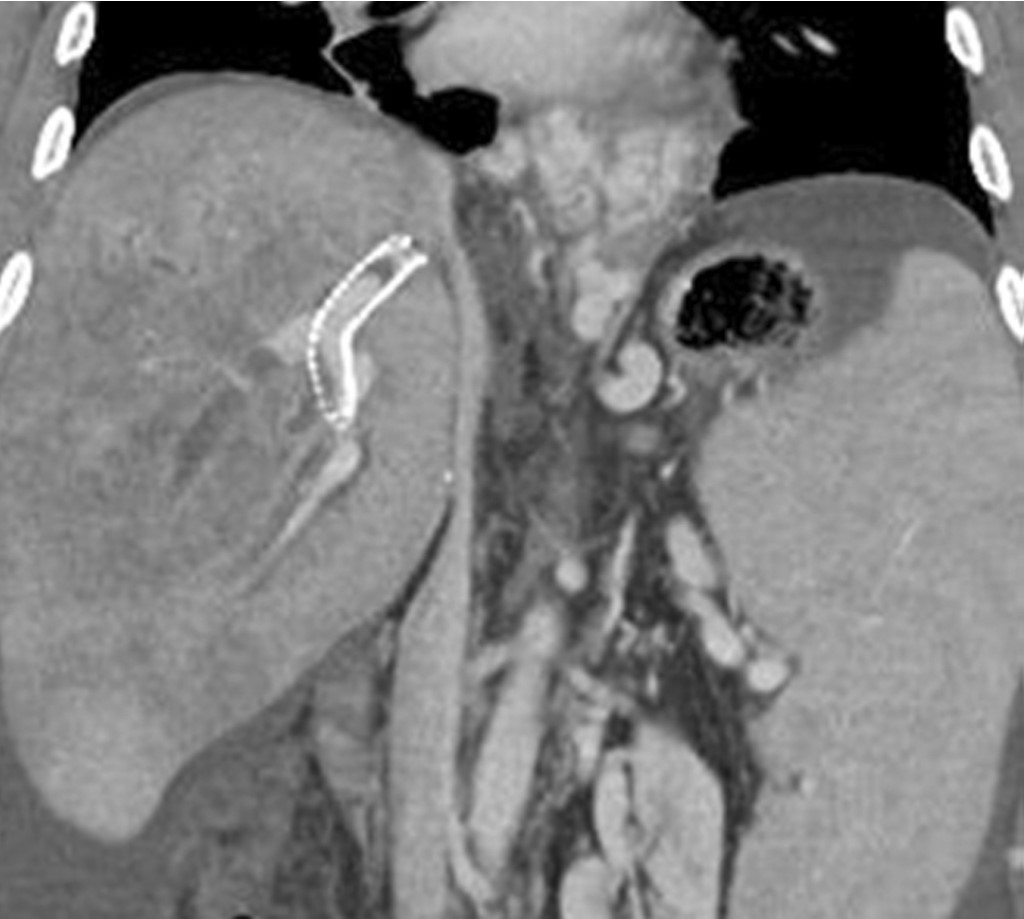
생체간이식 수술 1년 후 시행한 복부 CT에서 우간정맥 (right hepatic vein)은 개통되어 있으나 5번 분절(sgment)과 8번 분절 간정맥을 하대정맥과 연결하는 이식혈관은 폐색되어 있으며 문맥압항진증으로 인해 복수가 증가하였음. 목정맥경유간생검 조직검사에서 만성거부반응이 나왔음. 난치성 복수와 식도정맥류 출혈의 치료를 위해 TIPS를 시행하였음. TIPS시술 6일 후 시행한 복부 CT에서 TIPS 경로의 원위부에 부분 폐색이 관찰되며 우간정맥 혈전증에 의한 간 울혈의 소견으로 불규칙한 저음영 병변들이 관찰됨 (Fig 1).
Fig. 1.
CT scan obtained on 6 days after TIPS show partial occlusion of distal end of the TIPS stent, and ill defined low density in the liver due to hepatic vein thrombosis.
시술방법 및 재료
우측 속목정맥 (right internal jugular vein)을 천자하여 안내철사로 TIPS 경로를 통과한 다음 5-Fr 카테타로 시행한 간문맥 조영술에서 TIPS 경로 말단부에 부분폐색이 관찰되며 우간정맥 내에 혈전 소견이 보임(Fig 2, 3). 8 mm 직경 풍선카테타 (Foxcross, Abbott, Beringen, Switzerland)와 6-Fr 안내카테타(Envoy, Cordis, Florida, USA)를 이용하여 간정맥 내의 혈전을 maceration한 후 흡입하여 제거하였음(Fig 4). TIPS 경로 말단부 부분폐색을 해결하기 위해 추가적인 bare metal stent (Taewoong medical, Gyeonggi-do, Korea)를 간정맥대정맥 접합 (hepatocaval junction)부위까지 확장하여 설치하였음 (Fig 5). 시술 후 빌리루빈 수치는 점진적으로 감소하여 시술 2주일 후에는 2 mg/dl까지 감소하였음. 간정맥 혈전제거술 4개월 후 시행한 복부 CT에서 우간정맥은 재개통되었으며 간 울혈의 소견도 호전되었음 (Fig 6).
Fig. 2.
Portogram shows partial occlusion in the distal end of the TIPS stent.
Fig. 3.
Right hepatic venogram shows filling defect suggesting thrombus.
Fig. 4.
Right hepatic vein thrombosis was markedly improved after balloon maceration and aspiration thrombectomy.
Fig. 5.
Portogram after insertion of an additional stent demonstrates patent TIPS tract.
Fig. 6.
CT scan obtained 4 months after procedure shows complete improvement of hepatic congestion, and patait right hepatic vein.
고찰
급성 Budd-Chiari syndrome은 급성 간정맥 혈전증으로 인해 발생하며 주로 경구피임제 혹은 선행혈전질환과 연관이 있고 서양인에서 호발한다. 때로는 본 증례와 같이 의인성으로도 발생할 수 있으며 황달, 간성뇌증을 일으킬 수 있고 심하면 간부전이 올 수 있다. 급성 Budd-Chiari syndrome은 치료 목표는 간울혈을 조기에 완화시켜 간기능을 보존하여 급성간부전을 예방하고 문맥고혈압증으로 이행을 막는 것이다. 급성 Budd-Chiari syndrome의 혈관내 치료에 대한 보고는 많지 않으나 혈전이 오래되지 않은 경우 기계적 혈전제거술을 병행한 약물혈전용해술이 효과적이다. 본 증례의 경우 식도정맥류출혈이 있어 혈전용해술을 시행하지 못하였으며 흡입 혈전제거술 만으로도 성공적으로 간울혈을 치료하여 간부전으로의 진행을 막을 수 있었다. 생체간이식후 문맥고혈압의 발생은 바이러스성 간염의 재발이나 이식거부반응에 의해 일어나며 간재이식술을 기다리기 전 문맥고혈압에 의한 합병증이 발생시 TIPS를 시행할 수 있다. 그러나 생체간이식 환자에서 TIPS는 기술적으로 어려우며 보고에 의하면 시술 후 간 괴사의 가능성이 있고 간성뇌병증의 빈도도 높다. 또한 본 증례와 같이 우간정맥만 간의 배출정맥으로 개통되어 있는 경우 TIPS시술 후 급성 간정맥 혈전증에 의한 Budd-Chiari syndrome의 발생 가능성이 있으므로 주의를 기울여야 한다.
참고문헌
1. Schemmer P, Radeleff B, Flechtenmacher C, et al. TIPS for variceal hemorrhage after living related liver transplantation: a dangerous indication. World J Gastroenterol 2006; 12(3):493-5
2. Saad WA, Davis MG, Lee DE, et al. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt in a living donor left lateral segment liver transplant recipient: technical considerations. J Vase Interv Radiol 2005;16:873-7
3. Lee HJ, Kim KW, Mun HS, et al. Uncommon causes of hepatic congestion in patients after living donor liver transplantation. AJR 2009;193:772-80
4. Cura M, Haskal Z, Lopera J. Diagnostic and interventional radiology for Budd-Chiari syndrome. Radiographics 2009;29:669-81
5. Shama S, Texeira A, Texeira P, Elias E, Wilde J, Oliff SP. Pharmacological thrombolysis in Budd Chiari syndrome: a single centre experience. J Hepatol 2004;40:172-80
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by