중심단어
Venous thrombosis, kidney transplantation, mechanical aspiration thrombectomy
임상소견
Hypertensive nephropathy로 인한 chronic renal failure로 living donor kidney transplantation 시행받은 환자로 수술 후 14일경 both leg edema 발생하였으나 lymphedema 또는 postoperative change의 가능성 고려하여 투석하며 경과 관찰하던 중 left leg edema는 감소하였으나 right leg edema 악화되는 양상 지속되었다.
Right iliac artery and vein에 transplanted kidney의 renal artery와 두 가닥의 vein이 anastomosis되어 있는 상태이다.
영상소견
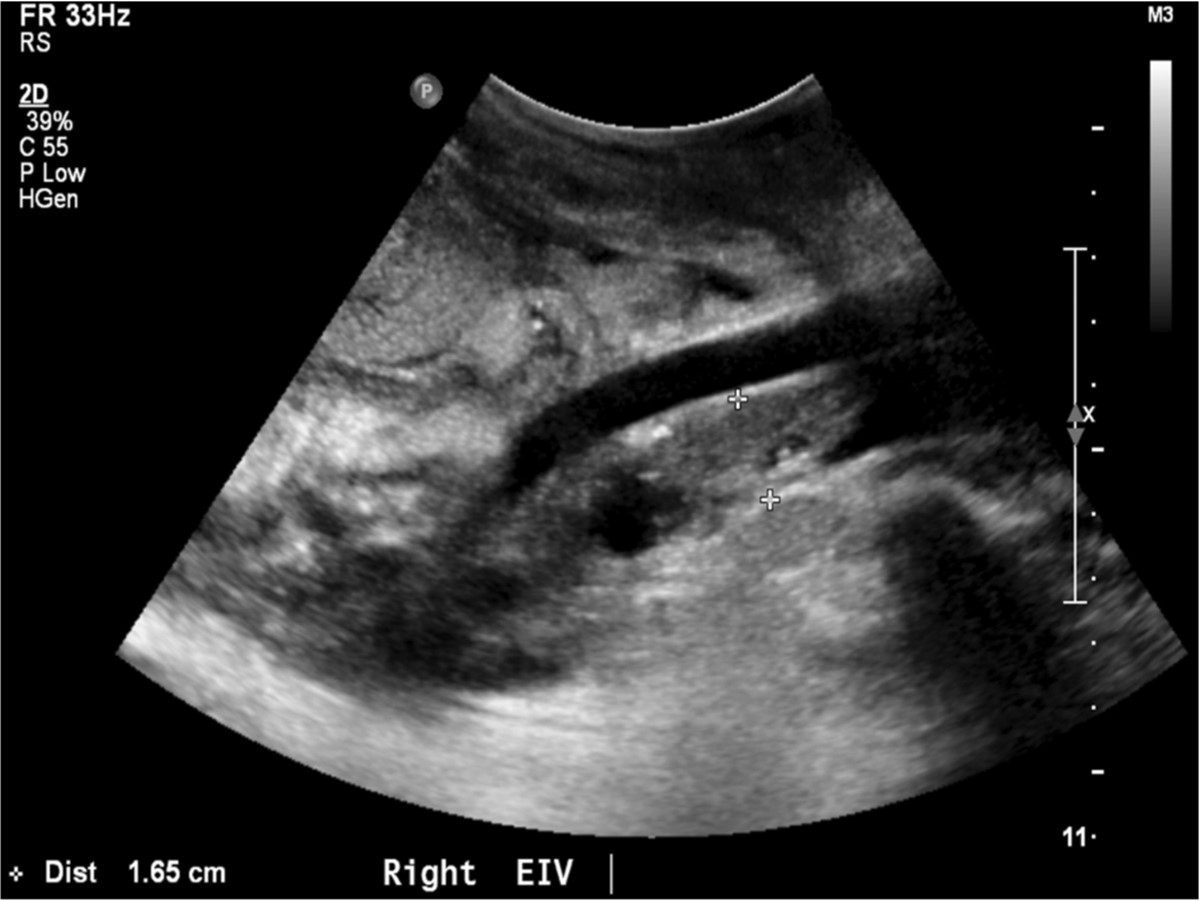
수술 직후 시행한 doppler US소견에서는 renal artery and vein에 flow abnormality가 없었으나, 수술 받은 뒤 약 20일 경에 시행된 doppler ultrasonography 상 right external iliac vein 전체가 thrombus로 인하여 total occlusion되어 있었다. Right common femoral vein 내부에도 massive thrombus로 인한 near total occlusion 상태로 partial flow를 유지하고 있었다(Fig. 1).
Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Ultrasonography demons tated completely occlusive thrombus with in the right external iliac vein.
시술방법 및 재료
Right common femoral vein thrombus를 피해 초음파 유도하에 distal femoral vein을 천자하였다. 8F sheath를 insertion 한 뒤 venogram시행하였으며, right external iliac vein과 right common iliac vein에 extensive thrombosis가 있었고 venous flow는 모두 아래쪽으로 역류하여 groin 근처에 발달한 collateral vein을 통해 drain 되고 있었다(Fig. 2). Right external iliac vein에 renal vein 두 가닥이 연결되어 있었고 catheter를 renal vein내에 두고 시행한 venogram상 right external iliac vein thrombus 사이에 남아 있는 lumen을 통해 renal vein이 drain 되고 있었으며 renal vein자체에는 thrombosis가 없었다(Fig. 3).
Catheter를 renal vein의 anastomosis site 위쪽의 right external iliac vein으로 전진시켜 조영제를 주입해 보았을 때 anastomosis site 약 2 cm 위쪽에 tight stenosis가 있었다.
8F guiding catheter를 이용해서 mechanical aspiration thrombectomy를 시행하였고, stone basket과 Arrow-Trerotola device (Arrow-Trerotola PTD, Arrow Inti, US)를 사용하여 chronic thrombus를 maceration 시킨 뒤 aspiration을 시행하였다. 많은 양의 thrombus가 제거되어 venogram상 external iliac vein lumen이 많이 회복되었으나 residual thrombus를 모두 aspiration 하는 것은 더 이상 불가능할 것으로 판단되어 anastomosis site 약 2 cm 상방 right external iliac vein의 tight stenosis에 대하여 angioplasty를 시행하였다. Angioplasty를 시행할 경우 residual thrombus가 pulmonary embolism을 일으킬 수 있으므로, infrarenal IVC에 Vena cava filter (Gunther tulip, COOK, Bloomington, IN, US)를 설치해 둔 후, right external iliac vein의 tight stenosis를 14 mm balloon으로 angioplasty를 시행하였다(Fig. 4). 그러나 balloon이 deflation 되면서 즉시 elastic recoil이 관찰되어 angioplasty에 반응하지 않는 병변으로 판단되었지만, flow가 충분히 유지되고 있고, 환자의 나이가 젊어 stent insertion 시행하지 않고 시술을 종료하였다(Fig. 5).
시술 뒤 환자의 우측 하지 부종은 회복되었으며, 2주일 후 follow up angiography를 시행하였다(Fig. 6). Venogram상 renal vein과 iliac vein의 flow가 많이 개선되었고, residual thrombus는 사라졌으며, collateral vein도 모두 소실되었다. 그러나 right external iliac vein의 tight stenosis는 여전히 residual stenosis가 남아 있어 추가적 balloon dilatation을 시행하였다. 시술 2개월 뒤 IVC filter를 제거하면서 시행한 venogram상 우측 EIV에 여전히 residual stenosis는 남아있지만 flow에 장애가 없고 증상이 없어, 향후 venous return 자체에는 큰 문제가 없을 것으로 보였다(Fig, 7). 이후 환자는 외래에서 더 이상의 증상 악화나 하지 부종 없이 지내고 있다.
Fig. 2.
Initial venography showed an occlusion of the right iliac vein and development of collateral vessels around the occluded vein.
Fig. 3.
Venogram showed patent two renal veins anastomosed to the right external iliac vein.
Fig. 4.
Venography showed tight stenosis in right external iliac vein, we performed percutaneous transluminal angioplasty with 14 mm x 4 cm balloon catheter. After angioplasty with 6 atm, waist of stenosis disappeared. Immediate elastic recoil was found on post-procedural venography.
Fig. 5.
After percutaneous transluminal thromboaspiration and balloon angioplasty, improvement in lumen diameter with residual thrombosis and residual narrowing from elastic recoil.
Fig. 6.
14 days after percutaneous transluminal thromboaspiration and angioplasty, Follow up venography demonstrated patent iliac vein flow with disappearance of collateral vessels. Tight stenosis in right external iliac vein still remained.
Fig. 7.
After repeated balloon angioplasty, post-procedural venography showed improvement in lumen diameter with residual stenosis.
고찰
Major surgery를 받은 환자에서 deep vein thrombosis (DVT)는 pulmonary embolism, pulmonary hypertension, lower extremities의 chronic venous insufficiency를 초래할 수 있는 심각한 합병증이다. 본 증례는 신이식을 받은 직후 ipsilateral subacute iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis가 발생한 경우로서 발생 빈도는 극히 낮아 증례 보고 형식으로만 알려져 있고, 이는 allograft failure 또는 rupture등 심각한 합병증을 초래할 수 있다. Thrombosis는 수술 후 2주에 가장 빈도가 높으며 원인은 pediatric donors, multiple renal veins, prolonged ischaemic time, delayed graft function, extrinsic compression, torsion, hypotension/hypoperfusion등이 있다. 또한 acute rejection, glomerulonephritis, immunosuppressive therapy에 의해 이차적으로 late thrombosis가 발생할 수 있다. 특히 end-stage renal disease 환자에서 antiphospholipid antibody의 상승은 흔하며 hypercoagulable states를 초래한다. 원인이 무엇이든 간에 조기 진단이 allograft failure를 방지하는데 중요하다. Duplex ultrasonography는 initial test of choice로 iliofemoral veins과 renal allograft venovenostomy site의 혈류를 평가할 수 있다. Venography는 진단의 gold standard 이지만 acute renal allograft dysfunction 상태에서는 조영제 사용으로 인해 제한이 있다. 일반적인 DVT와 달리 신이식 후에는 출혈의 위험과 신기능의 저하로 치료에 제약이 따른다. 일반적으로 신이식 환자에서 acute DVT의 treatment of choice는 thrombolytic therapy이지만 약 10% 에서 hemorrhagic complication이 발생한다, Renal dysfunction이 등반된 early renal allograft vein thrombosis의 경우는 pulmonary embolism과 높은 DVT 재발률의 위험이 있음에도 불구하고 surgical thrombectomy도 고려할 수 있다. 그러나 본 증례의 환자의 경우에는 thrombus를 aspiration했을 때 fresh thrombosis가 아닌 organized thrombus가 나와 적어도 일주일 이상은 경과된 것으로 판단되었으며, 수술 후 30일 이내에 진단이 되었기 때문에 출혈 위험을 고려하여 thrombolysis는 시행하지 않고, mechanical aspiration thrombectomy만 시행하였다. Hwang et al,[2]은 신 이식 직후 발생한 ipsilateral acute iliofemoral DVT에 대하여 carbon dioxide를 contrast medium으로 사용한 percutaneous transluminal thromboaspiration을 통해 성공적으로 시행한 증례를 보고하였다.
신이식 직후 발생한 iliofemoral deep vein thrombosis는 드물지만 allograft failure를 초래할 수 있어 조기진단이 필수적이며 환자의 신기능과 출혈 위험 정도에 따라 치료방법의 적절한 선택이 요구된다. 본 증례에서와 같이 percutaneous transluminal thromboaspiration은 안전하고 효과적인 치료방법으로 생각되지만 현재까지는 소수의 케이스에 대한 연구보고만 있기 때문에 장기적 연구가 필요할 것으로 생각된다.
참고문헌
1. Sterrett SP, Mercer D, Johanning J, Botha JF. Salvage of renal allograft using venous thrombectomy in the setting of iliofemoral venous thrombosis. Nephrol Dial Transplant 2004;19:1637-1639
2. Hwang JK, Chun HJ, Moon IS, Kim JI. The Treatment of Deep Vein Thrombosis Immediately After Kidney Transplantation: A Case Report. Transplant Proc 2011 ;43:2415-2417
3. Ramirez PJ, Gohh RY, Kestin A, Monaco AP, Morrissey PE. Renal allograft loss due to proximal extension of ileofemoral deep venous thrombosis. Clin Transplant 2002;16:310-313
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by