중심단어
Celiac artery stenosis, pancreaticoduodenectomy, stent
임상소견
Pancreatic head cancer로 수술 중 GDA를 묶고 specimen을 적출한 후 hepatic artery로의 blood flow가 소실되어 혈관조영실로 연락.
진단명
Celiac artery stenosis
영상소견
수술 전 시행한 CT를 다시 review했을 때, celiac artery의 입구가 arcuate ligament에 의해 눌린 모습으로 매우 좁아져 있으며 pancreaticoduodenal arcade의 hypertrophy가 보임 (Fig. 1). Celiac artery stenosis가 있어 SMA에서 pancreaticoduodenal arcade를 통해 GDA의 blood flow의 방향이 역전되어 hepatic artery로 혈류를 공급하는 상황에서, 수술 중 GDA의 flow를 차단시키자 hepatic artery 의 perfusion이 소실 된 것으로 보임.
Fig. 1
CT images showed celiac artery stenosis (arrow) and hypertrophied pancreaticoduodenal arcade (arrowhead).
시술방법 및 재료
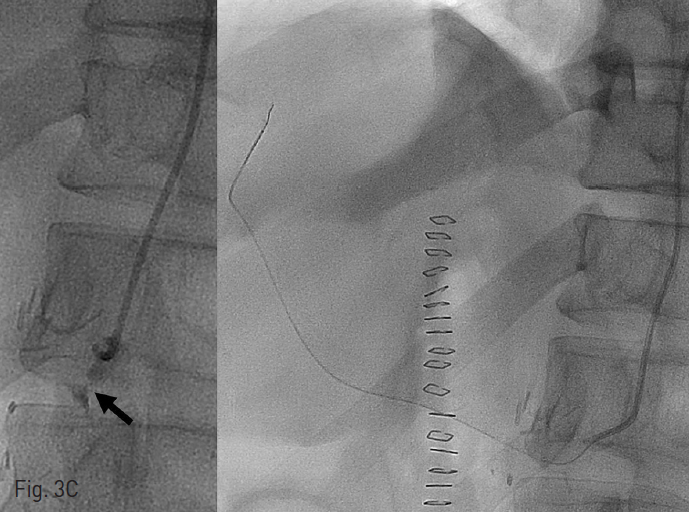
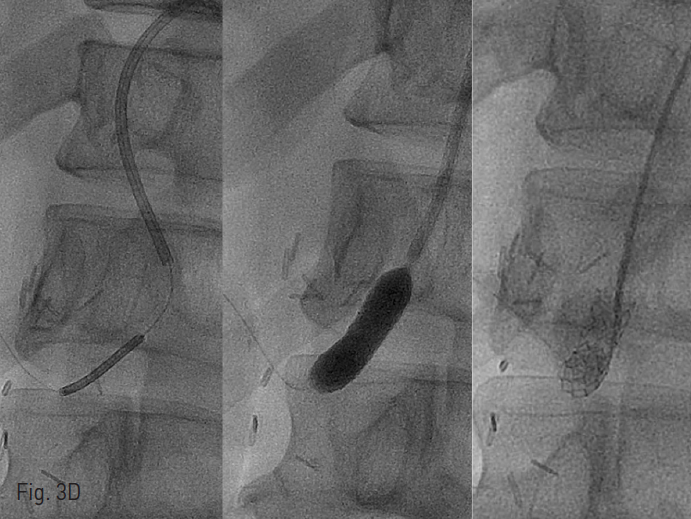
수술 중 곧바로 혈관조영실로 이동하였고, right common femoral artery를 통해 6Fr sheath를 retrograde insertion한 후 pigtail catheter를 이용해서 abdominal aortography를 시행했을 때, celiac artery로 flow는 약간 보이지만 매우 느려져 있는 것을 볼 수 있음 (Fig. 2). 이에 RH catheter를 이용하여 celiac artery를 selection하였지만, arcuate ligament에 의한 눌림으로 celiac artery가 acute downward direction을 보여, 0.035 wire가 통과되지 못함 (Fig. 3A). 이에 microwire를 통과시킨 후, microballoon을 이용하여 angioplasty를 시도했지만, microballoon 조차도 acute angle을 극복하지 못함(Fig. 3B). 이에 Lt brachial artery에 6Fr sheath를 새로 insertion한 후, 6Fr catheter와 4Fr catheter를 coaxial로 삽입하여 celiac artery를 selection하였고 (Fig. 3C), microwire를 좁아진 celiac artery를 통과시킨 후, 7mm x 24cm balloon ex pandable stent를 삽입함 (Fib. 3D). 이후 시행한 angiography에서 celiac artery를 통한 blood flow가 완전히 회복된 것을 확인하고 환자를 수술장으로 돌려보냄.
Fig. 2
Early phase (A) and delayed phase (B) of abdominal aortogram showed very slow blood flow through celiac artery comparison with both renal arteries.
Fig. 3. Celiac artery stenting
A. RH catheter was advanced through the stenotic lesion of celiac artery with acute downward angulation. However, it was impossible to insert 0.035 wire up to hepatic artery.
B. To try balloon angioplasty temporally, microcatheter and a microwire was inserted to the liver. However, even a microballoon catheter could not be inserted over the microwire. It was because the wire was too stiff and thick to maneuver these double angles (arrow).
C. After gaining another access through the left brachial artery, celiac artery was selected using 6Fr catheter again. There was the focal tight stenosis (arrow) with the contrast medium at celiac artery. The microcatheter was successfully inserted up to the hepatic artery again.
D. 7mm x 24mm balloon expandable stent could be inserted successfully. The stent was located at celiac trunk and is in a perpendicular position.
Fig. 4
The final abdominal aortogram showed that common hepatic artery (arrow) and its branches were enlar ged and even the enlarged GDA stump appeared (arrowhead). Unlike the initial aortogram, right hepatic artery was seen earlier than the SMA and both kidneys.
추적관찰
환자는 무사히 수술을 마쳤으며, 1년 이상의 추적관찰 CT에서 stent fracture 없이 혈류가 원활하게 유지되는 것을 확인함.
Fig. 5
On CT images taken one year after surgery, the stent precisely covers the celiac trunk without involvement of bifurcation (arrow). Blood flow through thestentis also intact up to the hepatic arteries (arrow head).
고찰
Celiac artery stenosis는 동양의 경우 arcuate ligament에 의한 extrinsic compression이 가장 흔한 원인이며, 이외에는 atherosclesosis나 혈관 주위에 커진 림프절에 의한 extrinsic compression이 원인이 될 수 있다. 비록 celiac artery stenosis가 있다 하더라도, pancreaticoduodenal arcade를 통해 SMA로의 collateral blood supply가 이루어지므로 임상적인 증상은 나타나지 않는다. 그러나, 본 증례의 경우처럼, 간담췌외과 영역의 수술을 받는 경우 GDA의 혈류가 차단되면 문제가 되기 때문에, 수술 전 CT검사를 통해 이를 확인하는 것은 매우 중요하겠다. 치료는 수술적으로 celiac artery 주위의 decompression을 시키는 것을 시도해볼 수 있지만, 오랜 기간의 extrinsic compression에 의해 이미 celiac artery가 손상을 받은 상태이므로 혈류의 회복을 기대하기는 어렵다. 수술적으로 다른 혈관으로의 연결을 시도해볼 수 있겠지만 endovascular treatment의 발달로 stent 삽입술을 시행하게 된다.
Celiac artery에 stent insertion을 하는 경우 호흡에 따른 횡격막의 움직임으로 인해 stent fracture가 발생하기 쉽기 때문에 self-expandable stent 사용을 추천한다. 그러나, 본 증례의 경우 응급상황에서 병원내 준비가 가능한 stent가 balloon expandable stent였기에 사용하게 되었으며, 이미 수술적으로 celiac artery 주위를 박리하여 decompression을 시도한 상태였으므로 stent fracture의 가능성은 낮을 것으로 예상하였다. Celiac artery stenosis의 많은 경우가 arcuate ligament에 의한 extrinsic compression이므로, 본 증례의 경우처럼 CFA를 통한 접근은 acute angle로 device의 통과가 어려운 경우가 많기 때문에, brachial artery 로의 접근을 선호하게 된다.
참고문헌
1. Park CM, Chung JW, Kim HB, et al. Celiac axis stenosis: incidence and etiologies in asymptomatic individuals. Korean J Radiol. 2001;2:8-13.
2. Sugae T, Fujii T, Kodera Y, et al. Classification of the celiac axis stenosis owing to median arcuate ligament compression, based on severity of the stenosis with subsequent proposals for management during pancreatoduodenectomy. Surgery. 2012;151:543-549.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by