중심단어
Percutaneous transesophageal gastrostomy (PTEG), enteral nutrition, tube feeding
한글 초록
위창냄술은 경구 섭취가 어려운 환자에게 장기간 튜브영양을 위해 널리 이용된다. 하지만, 간비장비대, 복벽과 위 사이에 끼인 결장, 위정맥류, 그리고 다량의 복수 등은 위창냄술을 시행하는 데 큰 걸림돌이 된다. 최근 기관지식도루를 동반한 식도암을 앓고 있는 67세 남성이 내과에서 경피적 내시경적 위창냄술 시행이 어렵다고 생각되어 경피적 영상유도 위창냄술 시행하기 위해 의뢰되었다. 우리는 시술 전 촬영한 복부 컴퓨터 단층촬영을 검토하였고, 간경화로 다량의 복수가 있고, 접근 경로에 문맥전신 곁가지들로 인한 확장된 혈관들이 관찰되어 경피적 영상유도 위창냄술 시행이 어렵다고 판단하였고 환자에게 Percutaneous transesophageal gastrostomy (PTEG)를 시행하였다. 상기 시술을 큰 합병증 없이 시행하였고, 환자는 튜브영양을 효과적으로 받을 수 있었다.
영문 초록
Gastrostomy is used to provide long term tube feeding to patients with inadequate oral intake. However, there are difficulties in performing gastrostomy in those with hepatosplenomegaly, interposed colon between abdominal wall and stomach, gastric varix and massive ascites etc. Recently 67-year-old man with esophageal cancer with broncho-esophageal fistula was referred from physicians for percutaneous radiologic gastrostomy (PRG) since percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy (PEG) was thought to be difficult. Prior to procedure, we reviewed abdominal CT and found massive ascites, and many dilated vessels due to portosystemic collaterals along the interventional pathway. PRG was thought to be difficult and PTEG was performed instead. Procedure was performed without significant complications and tube feeding to the patient was successful.
Introduction
위창냄술은 삼킴곤란과 같은 경구 섭취가 어려운 환자에서 장기간 튜브영양을 위해 널리 이용되고 있다. 경피적 내시경적 방법이 대부분 쉽게 시행되고 있지만, 내시경적 접근이 어려울 경우 경피적 영상유도 방법이 시행되고 있다. 하지만 간비장비대, 복벽과 위 사이에 끼인 결장, 위정맥류 그리고 다량의 복수 등은 경피적 영상 유도 위창냄술을 시행하는 데 있어서 큰 걸림돌이 된다. 저자들은 간경화로 다량의 복수와 복벽에 발생한 확장된 혈관들로 인해 위창냄술 시행이 어려웠던 환자에게 percutaneous transesophageal gastrostomy (PTEG)을 시행하였고 효과적으로 장기간 튜브영양이 가능하였기에 방법과 효용성을 공유하고자 한다.
Case report
증례
67세/남자
임상소견
간경화, 당뇨 병력이 있었으며, 최근 식도암으로 고식적 방사선 치료, self-expandable metallic stent 삽입을 받고 지내던 중 기관지식도루가 발생하였다. stent 제거 후 내과적으로 경피적 내시경적 위창냄술을 시행하는데 어려움이 있어 경피적 영상유도 위창냄술 시행하기 위해 인터벤션에 자문의뢰 되었다.
진단명
Esophageal cancer with broncho-esophageal fistula.
영상소견
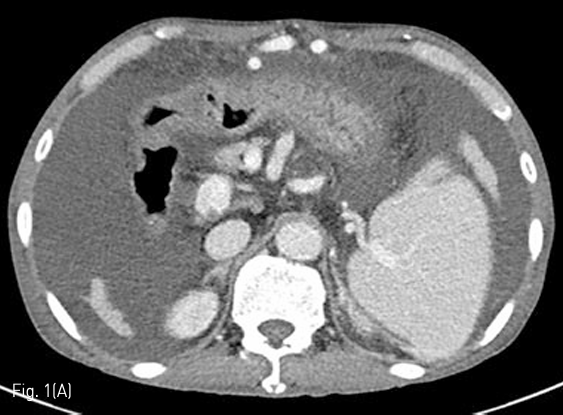
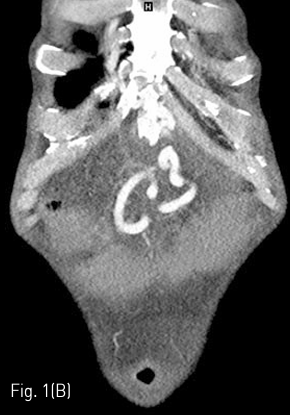
경피적 영상유도 위창냄술을 시행하기 위해 시술 전 촬영한 복부 컴퓨터단층촬영을 검토하였고, 환자는 간경화로 다량의 복수가 있고, 접근 경로에 문맥 전신 곁가지들로 인한 확장된 혈관들이 관찰되었다 (Fig. 1). 경피적 영상유도 위창냄술을 시행하는 것이 어렵다고 판단하였고 환자에게 Percutaneous transesophageal gastrostomy (PTEG)를 시행하기로 결정하였다.
시술방법 및 재료
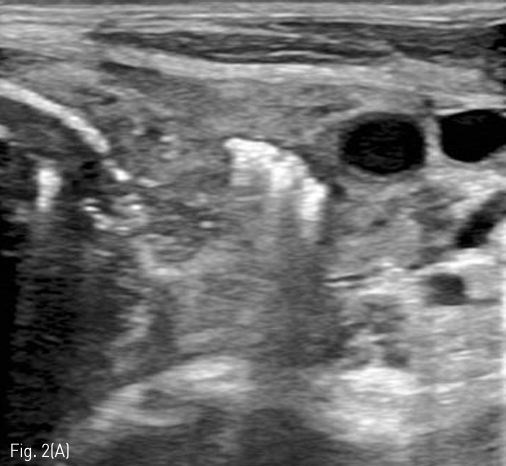
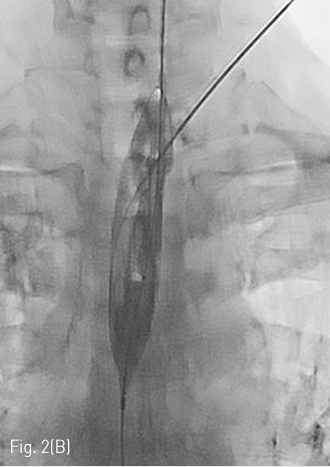
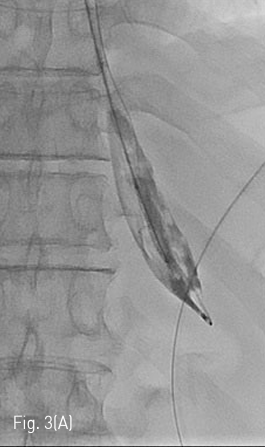
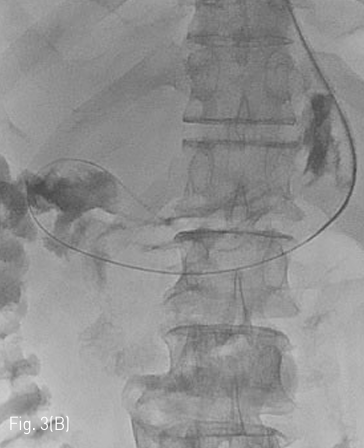
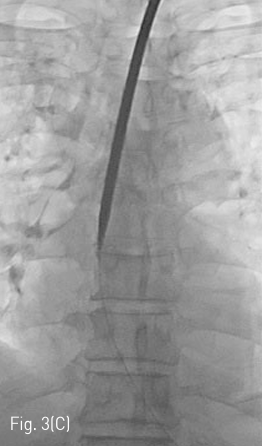
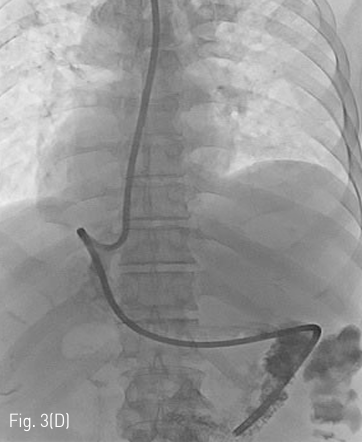
Fluoroscopy 유도하에 경구를 통해 0.035 인치 유도철사 (Glidewire, Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)를 위 속까지 삽입한 후 20mm x 4cm 풍선카테터 (Atlas, BARD, Arizona, USA)를 흉곽입구식도 중간부위에 위치하도록 하였다. 조영제와 생리식염수를 혼합하여 풍선카테터를 팽창시켰고, 초음파 유도하에 팽창된 풍선을 percutaneous transesophageal approach 하여 18게이지 바늘 (Chiba biopsy needle, Cook, Bloomington, USA)로 천자하였다(Fig. 2. A-B). 천자 바늘의 속심을 제거한 후 조영제가 역류되는 것을 확인하였다. J-tip 유도 철사 (J-Tip Glidewire, Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)를 터진 풍선 내로 전진시키고, 터진 풍선과 J-tip 유도철사를 식도하부 혹은 위 안쪽에 위치시킨 후(Fig. 3A) 터진 풍선과 입을 통해 삽입되었던 0.35 인치 유도철사를 제거하고 transesophageal J-tip 유도 철사만 남겨 놓았다. (Fig. 3B) 순차적으로 12Fr, 14Fr dilators (Dilator, Cook, Bloomington, USA)를 이용하여 tract을 확장 시켰다. 18Fr 분리 제거형집(Enteral access dilation system, HALYARD, Alpharetta, USA)을 거치한 뒤 (Fig. 3C) 14Fr 빈천자창냄 카테터(MIC; jejunal feeding tube, HALYARD, Alpharetta, USA)를 십이지장내 세번째 부위까지 진입시키고 분리제거형집을 제거하였다(Fig. 3D). 삽입된 카테터는 목 피부에 봉합하여 고정하고 시술을 종료하였다.
추적관찰
환자는 예방적 항생제를 복용하였고, 시술 4일 후 튜브영양을 시작하였다. 큰 합병증 없이 퇴원하였고, 시술 약 3주 후 인터벤션 외래 방문하여 14Fr Levin tube로 교환 시행하였다.
Fig 1A
Axial (A) and coronal (B) CT shows large amount of ascites and tortuous dilated vessels between abdominal wall and stomach at access route.
Fig 1B
Axial (A) and coronal (B) CT shows large amount of ascites and tortuous dilated vessels between abdominal wall and stomach at access route.
Fig 2A
(A) On US, inflated balloon with a mixture of normal saline and contrast medium (long arrow) is seen echogenic in the esophagus between Lt. common carotid artery (dotted arrow) and Lt. thyroid gland. (short arrow)
Fig 2B
(B) On fluroscopy, the position of inflated balloon is adjusted between the thoracic inlet and Lt. clavicle. Under US guidance, the Balloon is punctured with an 18 G puncture needle through the left neck.
Fig 3A
(A) J-tip guidewire is inserted so that the tip of it was retained within the ruptured balloon. The ruptured balloon is then advanced along with 0.035 inch guidewire into the stomach.
Fig 3B
(B) The tip of the J-tip guidewire is then dislodged from the ruptured balloon and after deflation, the ruptured balloon catheter and 0.035 inch guidewire are removed to leave only the J-tip guidewire.
Fig 3C
(C) After gradually increasing size of dilatation via 12Fr and 14Fr dilators, 18Fr peel away sheath is inserted over the J-tip guidewire.
Fig 3D
(D) After sufficient dilatation, the dilator is removed to leave only the J-tip guidewire and the external sheath in place. A 14Fr jejunostomy catheter is then inserted over the J-tip guidewire via the external sheath. After removing the guidewire, contrast medium is injected into catheter to confirm that the tip of the tube was placed appropriately.
고찰
튜브영양은 삼킴곤란이 있는 환자, 경구 섭취가 불가능할 때에 충분한 경관 영양을 유지하기 위해 필요하다. 대부분 초기에 비위관이 이용되지만, 장기간 유지 시 피부경유경로가 대개 선호된다. 일반적으로 위창냄술은 안전하고 효과적이기 때문에 표준화된 피부 경유 경관영양 경로로 오랫동안 잘 사용되어 왔다. 하지만, 간비장비대, 복벽과 위 사이에 끼인 결장, 문맥압항진증 환자에서 정맥류, 그리고 다량의 복수 등이 있을 때에 시행하는데 적절하지 못하다. 이럴 경우 PTEG가 유용할 수 있으며, 이 시술은 1994년에 일본에 Oishi et al.에 의해 소개되었다. 초기에는 악성폐쇄가 있는 환자에서 위장 폐쇄를 감압 시킬 목적으로 시행되었지만, 이후에 위창냄술이 불가능하거나 위험한 환자에서, 대안으로 이용되었다. PTEG의 사망률은 기저 질환의 진행과 관련되는 경우가 대부분이라고 알려져 있다. 작은 합병증은 상처감염, 관주변 피부로 누출, 국한된 출혈, 관폐쇄, 피하 기종 등이 있다. 이러한 작은 합병증들뿐만 아니라, 복막염, 내부 장기 손상 등도 위창냄술과 비교하여 PTEG에서는 적은 것으로 알려져 있다. 위창냄술을 시행할 수 없는 장기간 튜브영양이 필요한 환자에서 PTEG는 유용하고 안전한 대안이 될 수 있다.
참고문헌
1. Udomsawaengsup S, Brethauer S, Kroh M, Chand B.Percutaneous transesophageal gastrostomy (PTEG): a safe and effective technique for gastrointestinal decompression in malignant obstruction and massive ascites. Surg Endosc 2008;22:2314-2318
2. Shin JH, Park AW.Updates on Percutaneous Radiologic Gastrostomy/Gastrojejunostomy and Jejunostomy. Gut and Liver 2010;4 suppl 1: S25-31
3. Rahnemai-Azar AA, Rahnemaiazar AA, Naghshizadian R, Kurtz A, Farkas DT. Percutaneous endoscopic gastrostomy: Indications, technique, complications and management World J Gastroenterol 2014;20:7739 7751
4. Toh Yoon EW, Nishihara K Percutaneous transesophageal gastro-tubing (PTEG) as an alternative long term tube feeding procedure when gastrostomy is not feasible. Therap Adv Gastroenterol 2017;10;911-917
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by