중심단어
Biopsy, percutaneous nephrostomy
국문 초록
신장 생검은 진단과 치료방침 결정을 위해 필수적인 침습적 술기다. 영상유도 하의 흡인 생검이 신장 실질 질환의 진단에 이용되고 있으나, 병변이 비뇨기계 강내에 위치하거나 크기가 매우 작을 경우 시행하기 힘들다. 요관경을 통한 신우 병변의 생검은 낮은 민감도를 보인다. 경피적 신루술은 폐쇄성 요로 병증 환자에게서 시행되는 술기로, 이를 통해 생검을 시행할 수 있다. 이에 저자들은 경피석 신루술 길을 통해 악성 신우종양의 겸자 생검을 시행한 사례를 보고하고자 한다.
영문 초록
Renal biopsy is an essential invasive technique for establishment of the diagnosis and proper therapy planning. Image-guided percutaneous fine-needle aspiration biopsy is now an established diagnostic procedure in the different renal parenchymal diseases. Nevertheless, this method of tissue diagnosis is not fully justified for intra-urotract lesions or lesions which are often too small to allow an accurate puncture to obtain appropriate material. The accuracy of ureteroscopic biopsy has been reported as 56~94%, and sensitivity of pelvic lesion is much lower than the ureteral lesion. Percutaneous nephrostomy (PCN) is the procedure of choice for patients with obstructive uropathy. It can be used as an access to the urotract for biopsy instruments. Herein, the authors report a case of renal pelvic malignancy causing hydronephrosis for which tissue confirm was achieved by means of endoluminal forceps biopsy through the PCN tract.
Introduction
경피적 신루술 길을 통해 악성 신우종양의 겸자 생검을 시행한 사례를 보고하고자 한다.
Case report
증례
79세/여자
임상소견
환자는 우측 등 통증을 주소로 내원하였다. 신우종양 의심하에 경피적 흡인 생검을 시행 받았으나 병리적 진단에 충분한 조직을 얻지 못했다.
진단명
Urothelial cell carcinoma
영상소견
조영 증강 복부 CT에서 신우에 종양이 관찰되었고 수신증도 동반이 되어 있었다 (Fig. 1A, B). PET-CT상에도 병변에 FDG uptake가 증가되어 있었다 (Fig. 1C).
시술방법 및 재료
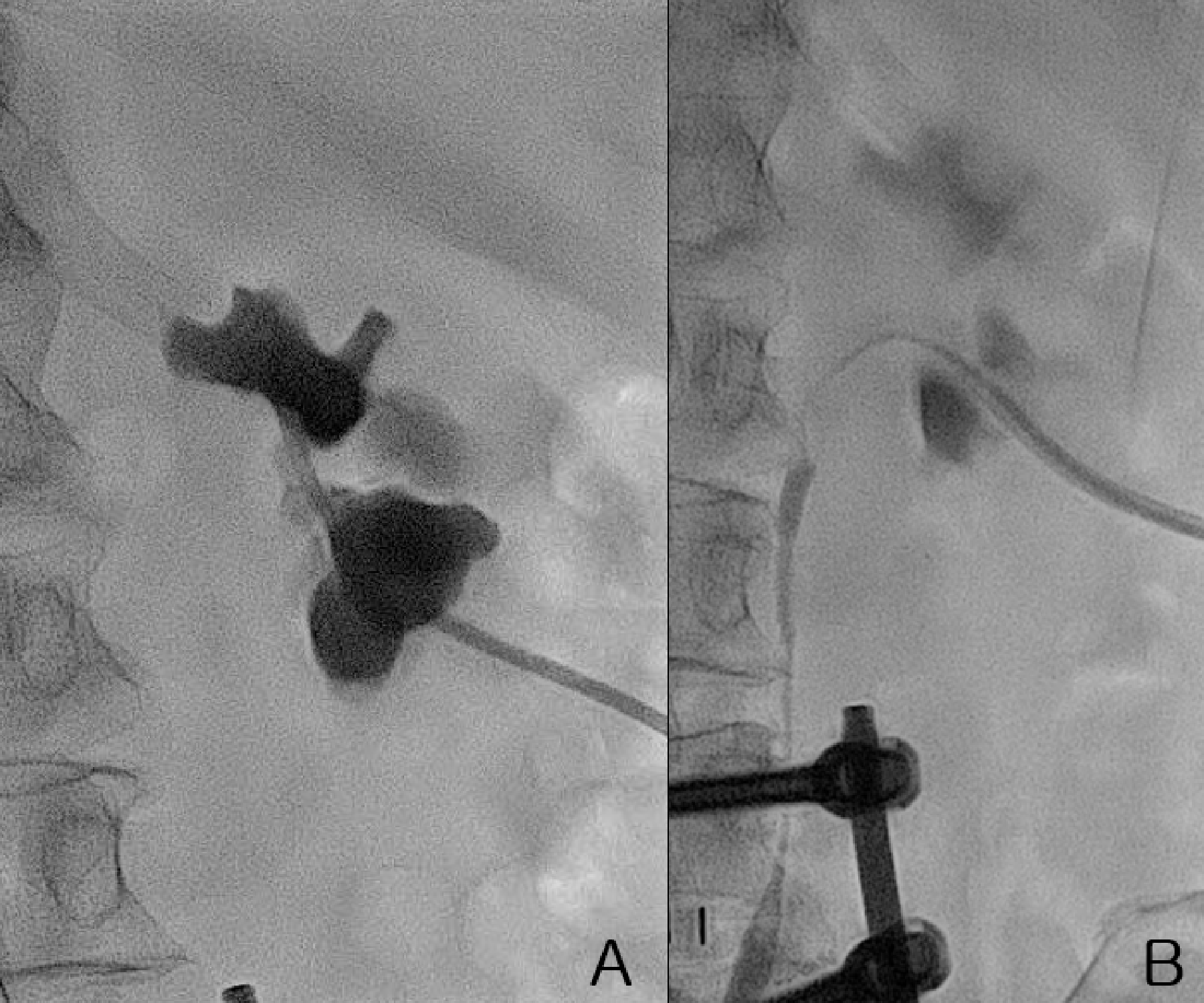
환자는 폐쇄성 요로 병증 치료를 위해 경피적 신루술을 시행 받고, 이후 경피적 신루술 길을 통한 조직 검사를 계획하였다. 국소 마취를 시행하고 시행한 하행성 신우 조영술에서 신우종양에 의한 신우와 요관 신우 이행부의 폐쇄를 확인할 수 있었으며 수신증의 동반도 확인할 수 있었다 (Fig. 2). 0.035-인치 유도 철사 (Terumo, Tokyo, Japan)를 삽입하여 기존에 설치된 8.5-F drainage catheter (Cook, Bloomington, IN)를 제거한 뒤, 5-F kumpe catheter (Cook, Bloomington, IN)와 유도 철사를 이용하여 병변을 지나 유도 철사를 요관에 위치시키다. 유도철사를 따라 8-F sheath (Teleflex, Wayne, PA)를 신우에 위치시키고 이를 통해 5.4-F biopsy forceps (Olympus, Southborough, MA)을 삽입하여 fluoroscopy 하에 신우 조영술 상의 신우 병변에 대해 5회 생검을 시행하였다 (Fig. 3). 이후 즉각적 합병증의 발생이 없는 것을 확인하고, 기존 8.5-F drainage catheter (Cook, Bloomington, IN)를 신우에 설치한 뒤 시술을 종료하였다.
추적관찰
병리 검사상 urothelial cell carcinoma로 진단되었다 (Fig. 4). 조영 증강 흉부 CT에서 목 임파선 전이가 확인되어 환자는 항암치료를 시행 받았다.
Fig. 1.
Fig. 1. Axial (A) and coronal (B) enhanced CT images show enhancing pelvic mass (arrow) causing hydronephrosis in right kidney. C. Axial PET-CT also demonstrates high FDG uptake in the pelvic mass (arrow).
Fig. 2.
Fig. 2. A, B. Antegrade pyelogram shows segmental obstruction in the renal pelvis and ureteropelvic junction.
Fig. 3.
Fig. 3. Spot radiography obtained during the procedure shows the biopsy forceps (arrow), which is inserted through a sheath to enable biopsy of the region of the stricture.
Fig. 4.
Fig. 4. A, B. Histologic examination of the biopsy specimen revealed urothelial cell carcinoma. A. pleomorphic nuclei (H&E, x 200). B. diffuse positive for CK7 (immunohistochemical staining, x100).
고찰
요관 내시경을 통한 생검은 상부 요로 종양의 진단에 표준화된 진단법이다. 그러나 그 정확도는 56~94%로 보고되고 있으며 신우 병변에 대한 민감도는 훨씬 낮다. 폐쇄성 요로 병변이 있는 환자의 대부분에서 경피적 신루술이 시행되며, 이를 통해 생검이 시행 될 수 있다. 조직 검사는 투시하에 시행한 신우 조영상에서 충만 결손으로 나타나게 되며, 초음파나 CT에서 종양이 관찰되지 않더라도 조직 검사를 시행해 볼 수 있다는 장점이 있다. Tsai 등은 8명의 환자에서 경피적 신루술 길을 통한 조직 검사를 성공적으로 시행하였다. 수혈이 필요 없는 일시적 혈뇨가 5명 (62.5%)에서 관찰되었으나, 천공이나 소변 누출과 같은 주요 합병증은 없었다. 그러므로 경피적 신루술 길을 통한 겸자 생검은 상부 요로 병변의 조직학적 진단에 유용할 수 있을 것으로 생각된다.
참고문헌
1. Tsai CC, Huang HT, Han SJ, Mo LR, Endoluminal Forceps Biopsy of the Urotract Disease Through a Percutaneous Nephrostomy Tract. Chin J Radiol. 2003;28:17-20
2. Roupr?t M, Babjuk M, Comp?rat E, Zigeuner R, Sylvester RJ, Burger M, et al. European Association of Urology Guidelines on Upper Urinary Tract Urothelial Carcinoma: 2017 Update. Eur Urol. 2018;73:111-122
3. Rojas CP, Castle SM, Llanos CA, Santos Cortes JA, Bird V, Rodriguez S et al. Low biopsy volume in ureteroscopy does not affect tumor biopsy grading in upper tract urothelial carcinoma. Urol Oncol. 2013;31:1696-1700
4. Renshaw AA. Comparison of ureteral washing and biopsy specimens in the community setting. Cancer 2006;108:45-48
5. Al-Qahtani SM, Legraverend D, Gil-Diez de Medina S, Sibony M, Traxer O. Can we improve the biopsy quality of upper urinary tract urothelial tumors? Single-center preliminary results of a new biopsy forceps. Urol Int. 2014;93:34-37
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by