중심단어
Liver cirrhosis, ascites, gastric varix, Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt, trans-splenic approach
국문 초록
목정맥경유간내문맥전신순환션트 (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt; TIPS) 후 추적 관찰 중 션트의 폐쇄가 발생한 경우 속목정맥 (internal jugular vein)을 통한 접근이 실패했을 때, 비장정맥으로 접근하여 효과적으로 치료한 증례를 보고한다.
영문 초록
We report a successful recanalization of Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt (TIPS) occlusion via trans-splenic approach after failed transjugular approach.
Introduction
목정맥경유간내문맥전신순환션트 (Transjugular Intrahepatic Portosystemic Shunt; TIPS)는 정맥류 출혈이나, 조절되지 않는 복수 등 간 문맥 고혈압의 증상이 있는 경우에 경피적으로 간정맥과 문맥 사이에 션트를 만들어서 문맥의 압력을 줄이는 시술이다(1).
션트의 개통성 (shunt patency)는 2년 추적시 76% 정도로 보고 되고 있으며, 우회로가 폐쇄되거나 좁아진 경우 재시술을 필요로 한다 (2,3). 이에, TIPS 후에 션트 폐쇄가 발생하여 일반적인 접근로인 속목정맥(internal jugular vein)을 통한 재개통이 실패한 환자에서 비장정맥으로 접근하여 성공적으로 재개통한 경우를 보고하고자 한다.
Case report
증례
56세/남자
임상소견
간경변 및 간암 환자로, 이전에 간암에 대해서 부분절제술 및 고주파소작술을 시행하였으며, 조절되지 않는 복수로 3개월 전에 TIPS을 시행하였다. 최근 복수량이 증가하고, 추적관찰 CT에서 션트의 폐쇄가 확인되어 재개통을 위해 의뢰되었다.
진단명
TIPS stent occlusion
영상소견
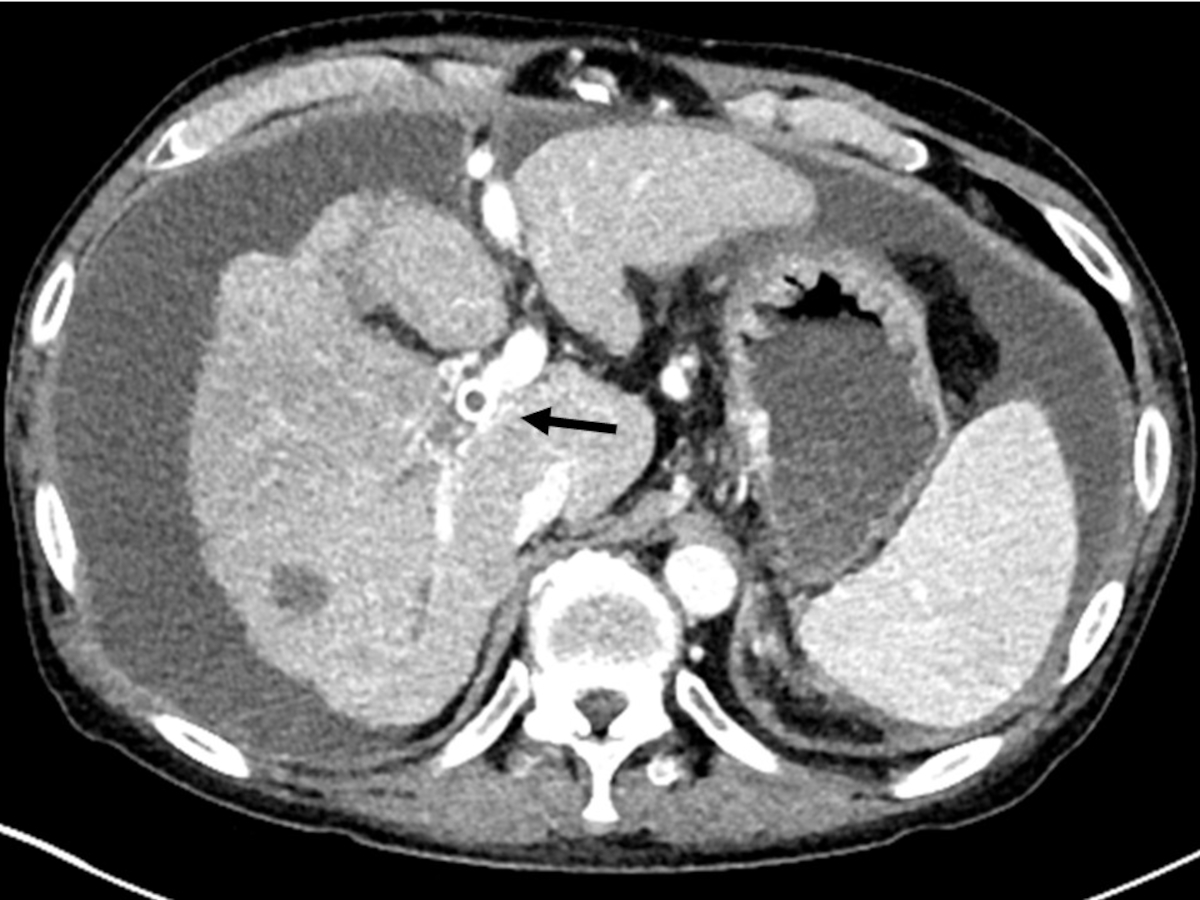
TIPS 시행 후 3달째 시행한 복부 단층촬영에서 션트는 막혀 있으며, 우문맥의 혈전이 보인다. 복부에 다량의 복수가 있다. (Fig. 1, 2).
시술방법 및 재료
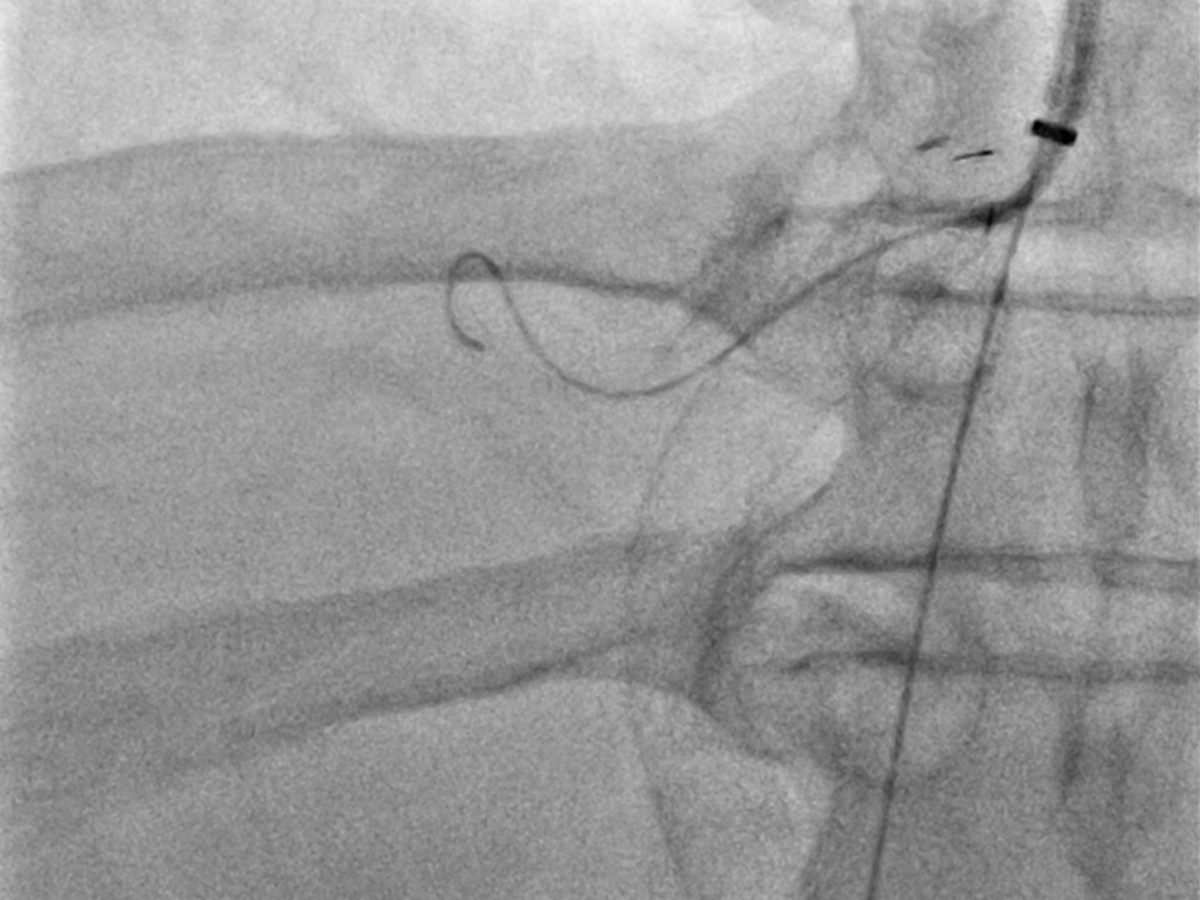
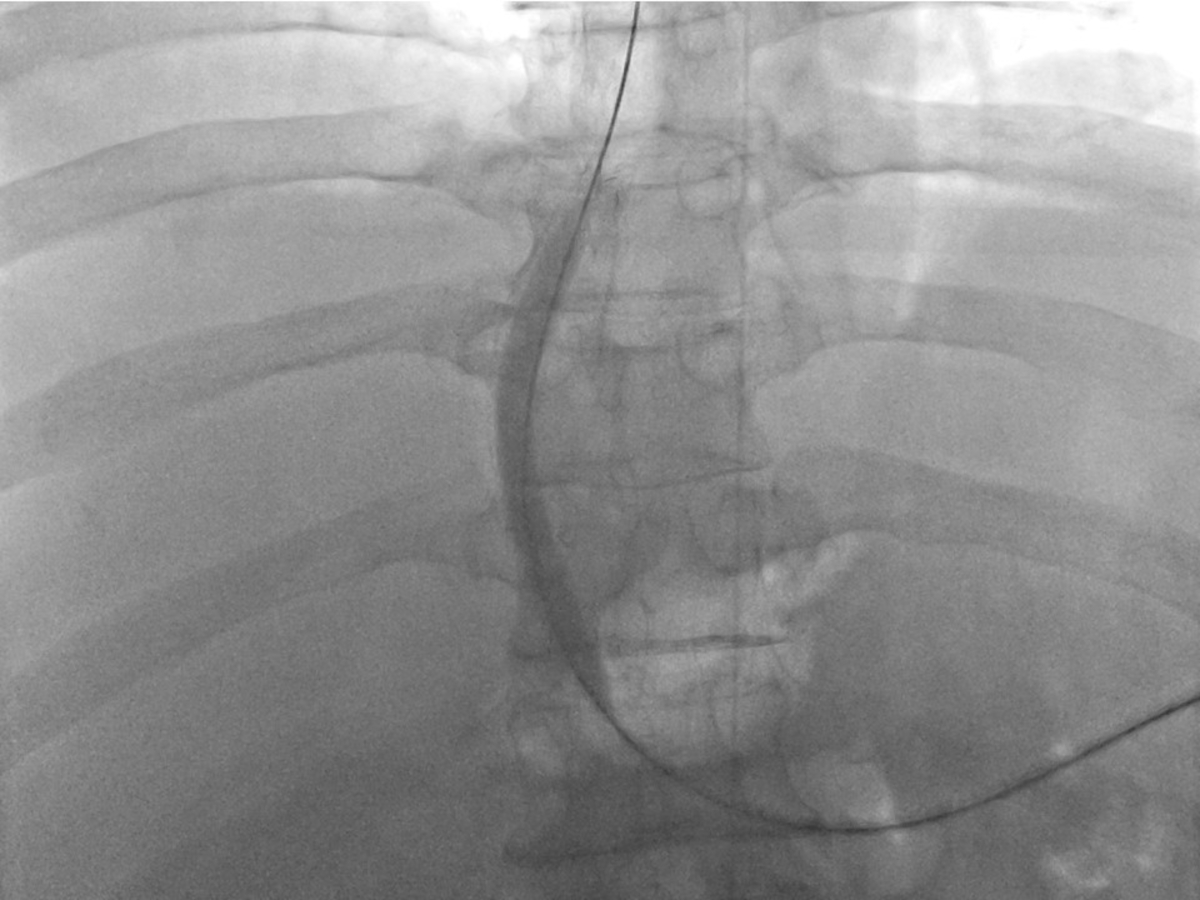
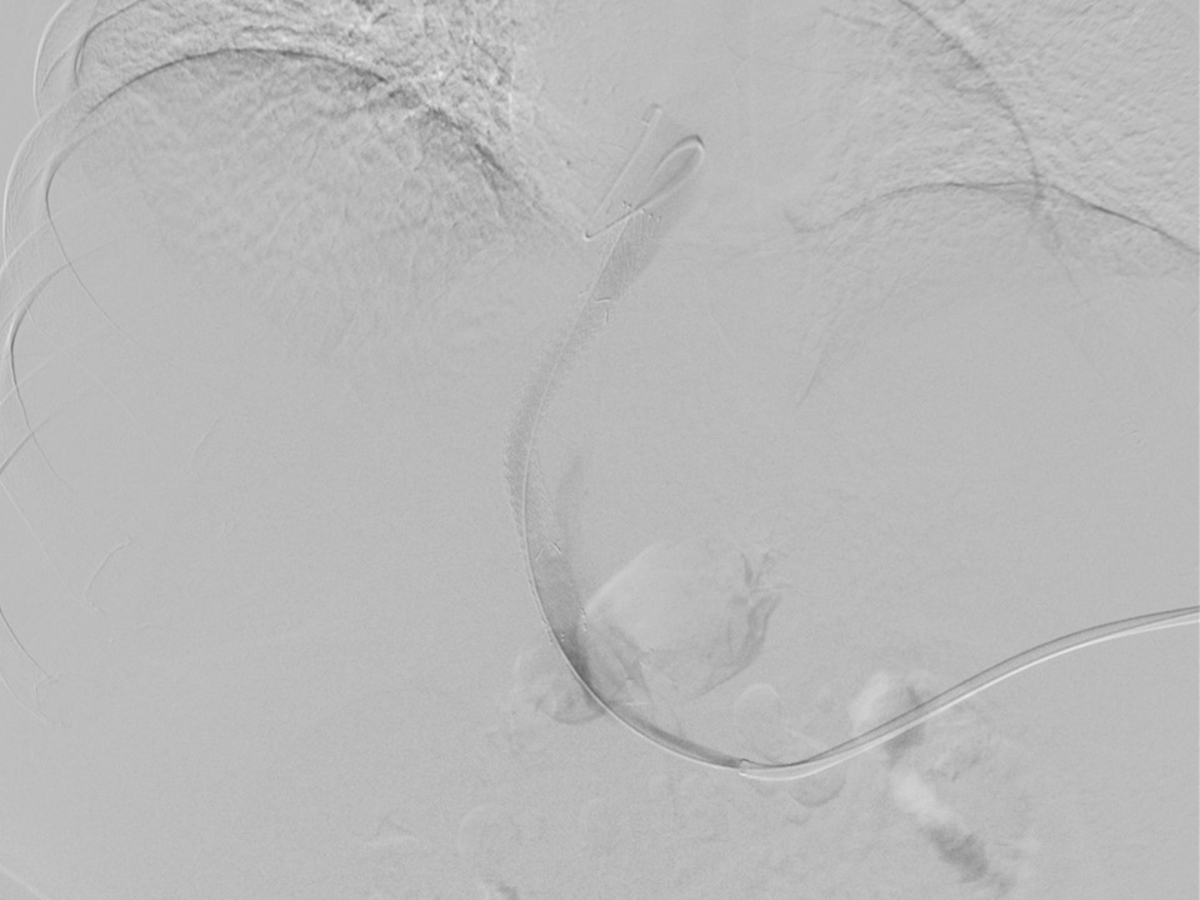
우측 속목정맥을 천자하여 우측 간정맥을 통해서 이전에 시술한 션트 스텐트 내강 내로 유도철사를 통과시키려 하였으나 스텐트 내부의 단단한 혈전으로 실패하였다 (Fig. 3). 이틀 뒤에 초음파 유도 하에 24-gauge Chiba needle (Duckwoo Medical, Gyeonggi-do, Korea)을 이용하여 비장 정맥을 천자하였고, 5Fr Cobra catheter (Cook, Bloomington, IN, USA)를 이용하여 시행한 간문맥 조영술에서 션트 스텐트는 막혀 있으며, 위식도 정맥류가 보인다 (Fig. 4). Cobra catheter를 이용하여 스텐트 내부를 선택하여 유도철사를 우심방까지 위치시켰다. 이후 8mm/8cm Balloon (Mustang Balloon catheter, Boston scientific, Natick, MA, USA)을 이용하여 풍선 확장술을 시행하였다. 확장술 시행 후 시행한 간문맥조영술에서 TIPS 스텐트의 혈류는 약간 개선되었으나, 식도 정맥류는 여전히 보여 션트 스텐트와 우심방에 걸쳐 8mm/10cm stent (EPICtm vascular self-expandable stent, Boston scientific, Natick, MA, USA)를 삽입하였고, 다시 풍선 확장술을 시행하였다 (Fig. 5). 이후 시행한 간문맥조영술에서 션트 스텐트로의 혈류는 재개통되었고, 위식도 정맥류는 보이지 않았다 (Fig. 6). 시술 후 비장 정맥 접근로에서의 출혈을 방지하기 위해서 coil (Nester, Cook)과 NBCA (Histoacryl®, B.Braun, Melsungen, Germany)을 이용하여 천자부위의 색전술을 시행하였다.
추적관찰
4개월 뒤 시행한 복부 CT에서 간암의 진행과 간기능의 저하로 복수는 관찰되었으나, 션트 스텐트의 혈류는 잘 유지되고 있었다 (Fig. 7, 8).
Fig. 1.
1 and 2. Axial (Fig. 1) and coronal (Fig. 2) CT images show a thrombosed TIPS stent (arrow and arrowheads). Massive ascites are also seen.
Fig. 2.
1 and 2. Axial (Fig. 1) and coronal (Fig. 2) CT images show a thrombosed TIPS stent (arrow and arrowheads). Massive ascites are also seen.
Fig. 3.
Guidewire selection was failed via transjugular approach due to severely thrombosed stent lumen.
Fig. 4.
Portal venography shows obliteration of the right portal vein and the appearance of gastric varices. TIPS flow was not seen (arrowheads).
Fig. 5.
Stent placement and post-stenting balloon dilatation are performed after the passage of obstructed segment with a guidewire, and the tip of the guidewire was placed at the right atrium.
Fig. 6.
Post-procedural portal venography demonstrates recanalized TIPS stent. Gastric varices were disappeared after recanalization.
Fig. 7.
Four months follow-up axial (Fig. 7) and coronal (Fig. 8) CT image shows patent TIPS stent (arrow and arrowheads).
Fig. 8.
Four months follow-up axial (Fig. 7) and coronal (Fig. 8) CT image shows patent TIPS stent (arrow and arrowheads).
고찰
목정맥경유간내문맥전신순환션트 이후 가능한 합병으로는 스텐트 기능저하가 가장 흔하고, 특히 스텐트의 폐쇄는 13~16% 정도로 보고되고 있다(4). 션트-간정맥 이행부위 또는 션트 내부 협착이 흔하며, 일반적으로는 속목정맥을 통한 풍선확장술 등으로 치료할 수 있다 (4, 5). 하지만, TIPS 폐색의 재개통 시에 풍선 확장술 단독으로만 시행되었던 경우는 20-30% 정도이며, 추가적인 스텐트의 삽입이 필요했던 경우는 60-70%로 보고되고 있다 (4). 션트 스텐트가 폐쇄된 경우에는 다양한 기법이 사용되고 있다. 내경정맥으로 접근하여 Colapinto 바늘을 이용하여 폐쇄된 스텐트 내부를 천자하여 재개통을 시키는 방법이 있으며, 성공률이 95%라는 한 보고가 있다 (6). 내경정맥을 통해 스텐트를 천자하고, 간문맥을 통해서 연결하는 방식도 사용할 수 있지만 이런 방식은 피복 스텐트 (covered stent)에서는 사용하기 어려운 점이 있다 (4). 비장정맥을 통한 접근 방법은 간문맥과 우회로를 좀더 일직선에 가까운 모양으로 접근할 수 있어서 폐쇄부분을 조금 더 쉽게 통과할 수 있었다. 비장정맥의 천자만 익숙하게 할 수 있으면 비교적 쉽게 시행할 수 있으며, 마지막으로 시술 부위를 microcoil이나 glue를 이용하여 잘 색전한다면 출혈이나 혈종 발생의 위험성을 줄이면서 시술을 시행할 수 있다.
참고문헌
1. Suhocki PV, Lungren MP, Kapoor B, Kim CY. Transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt complications: prevention and management. Semin Intervent Radiol. 2015 ;32(2):123-32.
2. Jirkovsky V, Fejfar T, Safka V, et al. Influence of the secondary deployment of expanded polytetrafluoroethylene-covered stent grafts on maintenance of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt patency. J Vasc Interv Radiol 2011;22(1):55-60
3. Bureau C, Pagan JC, Layrargues GP, et al. Patency of stents covered with polytetrafluoroethylene in patients treated by transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts: long-term results of a randomized multicentre study. Liver Int 2007;27(6):742-747
4. Ferral H, Banks B, Wholey M, Nazarian G, Bjarnason H, Casta?eda-Zu?iga W. Techniques for transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt revision. American Journal of Roentgenology. 1998;171(4):1041-1047.
5. Echenagusia M, Rodriguez-Rosales G, Simo G, Camu?ez F, Ba?ares R, Echenagusia A. Expanded PTFE-covered stent-grafts in the treatment of transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunt (TIPS) stenoses and occlusions. Abdom Imaging 2005;30(6):750-754
6. Miraglia R, Maruzzelli L, Luca A. Recanalization of occlusive transjugular intrahepatic portosystemic shunts inaccessible to the standard trans-venous approach. Diagnostic and Interventional Radiology. 2012; 19:61-65.
Citations
Citations to this article as recorded by